2025-07-11 理化学研究所,近畿大学,東京科学大学,量子科学技術研究開発機構,高エネルギー加速器研究機構,茨城大学,J-PARCセンター
<関連情報>
水素材料のメカノケミカル合成:格子歪みを有する水素に富むペロブスカイト型オキシヒドリドのアンモニア合成触媒としての利用 Mechanochemical Synthesis of H– Materials: Hydrogen-Rich Perovskite Oxyhydrides with Lattice Strain as an Ammonia Synthesis Catalyst
Fumitaka Takeiri,Norihiro Oshime,Shibghatullah Muhammady,Tasuku Uchimura,Hiroshi Yaguchi,Jun Haruyama,Akihiko Machida,Tetsu Watanuki,Takashi Saito,Kazuhiro Mori,Kenji Ohwada,Masaaki Kitano,and Genki Kobayashi
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: July 1, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c04467
Abstract
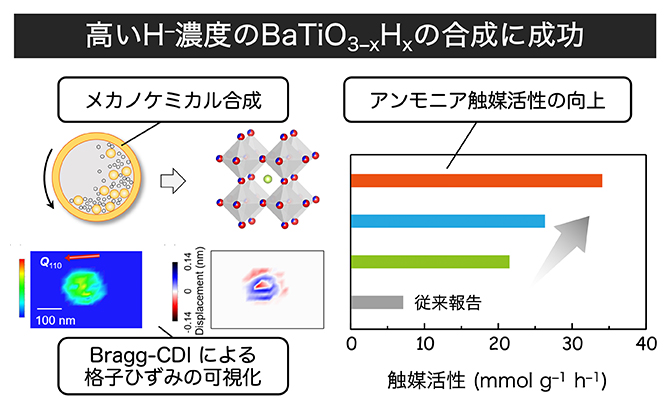
Mixed-anion perovskite compounds containing hydride ions (H–) are promising catalysts for ammonia synthesis under mild reaction conditions. Oxyhydride BaTiO3–xHx is a typical example, with a positive correlation between H– concentration x and catalytic activity; however, the previously reported topochemical synthesis achieved a maximum x value of ∼0.6. Herein, we significantly expand the H– solubility limit to ∼1 by using mechanochemical synthesis, wherein its nonthermal reaction condition enables oxyhydride formation rather than undesired metal-hydride formation and/or hydrogen desorption. The prepared Ru/BaTiO2H catalyst showed notable activity for ammonia synthesis (34 mmol g–1 h–1 at 400 °C and 0.9 MPa), which is much higher than that of the reported Ru/BaTiO2.5H0.5 catalyst. More surprisingly, when compared at the same H– concentration of x = 0.5, the mechanochemically prepared sample was approximately three times more active than the topochemically prepared sample. The Bragg coherent X-ray diffraction imaging (Bragg-CDI) technique revealed a non-negligible lattice strain in the mechanochemical product, not only at the surface but also inside the crystal, which is approximately ten times larger than that of the topochemical product, likely contributing to the enhanced catalytic activity. These findings indicate that mechanochemical synthesis enables the design of functional H–-based materials in terms of both the H– concentration and the lattice strain.