2025-06-26 中国科学院(CAS)
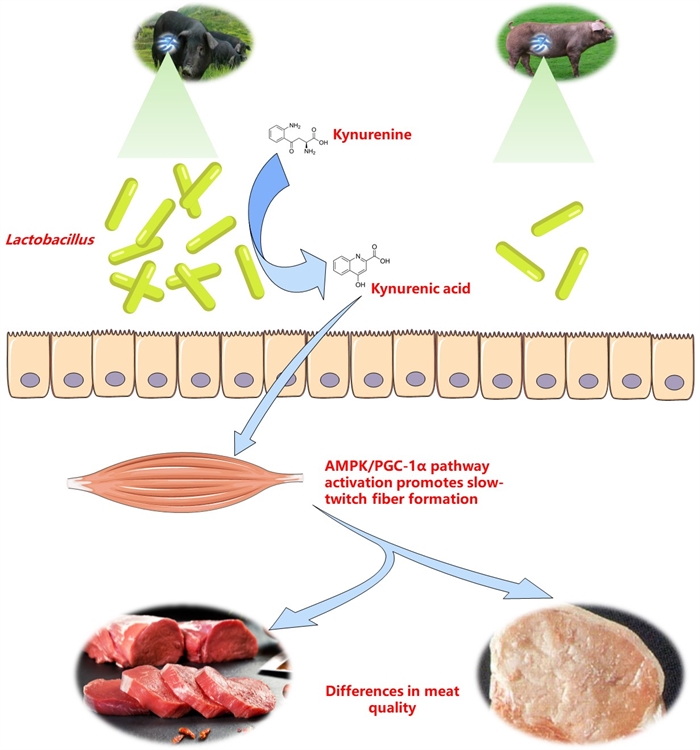
Gut microbiota identified as key to enhancing commercial pork quality (Image by SONG Bo)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/life/202506/t20250627_1046333.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41522-025-00745-3
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2023/fo/d2fo03709b
乳酸菌はトリプトファン代謝を介して中国原産ブタの筋線維型転換を制御する Lactobacillus regulate muscle fiber type conversion in Chinese native pigs via tryptophan metabolism
Bo Song,Md. Abul Kalam Azad,Qian Zhu,Yating Cheng,Sujuan Ding,Kang Yao & Xiangfeng Kong
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes Published:23 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41522-025-00745-3
Abstract
Identifying potential gut microbes and metabolites that can influence muscle fiber type is gaining interest in meat quality research. In this study, muscle fiber characteristics, muscle metabolite profiles, and gut microbiota and metabolome were compared among three pig breeds (Taoyuan black, TB; Xiangcun black, XB; and Duroc pigs). The results showed that the slow-twitch fiber percentage was higher (P < 0.05) in native pigs (TB and XB pigs) compared to Duroc pigs. The differences were mainly regulated by Lactobacillus abundance and tryptophan metabolism. Further, fecal microbiota transplantation from XB pigs transferred a higher slow-twitch fiber percentage, Lactobacillus abundance, kynurenic acid level, and AMPK/PGC-1α expression to mice. These findings suggest that Lactobacillus in the colon of TB and XB pigs, through kynurenic acid production, may promote slow-twitch fiber formation via the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway.
筋特性の比較と標的メタボローム解析から明らかになった豚3品種の枝肉形質と肉質の違い Muscle characteristics comparison and targeted metabolome analysis reveal differences in carcass traits and meat quality of three pig breeds
Bo Song,Yating Cheng,Md. Abul Kalam Azad, Sujuan Ding, Kang Yao and Xiangfeng Kong
Food & Function Published:21 Jul 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D2FO03709B
Abstract
This study investigated the molecular basis for differences in meat yield and quality between Duroc, Taoyuan black (TB), and Xiangcun black (XB) pigs. The results show that TB pigs have lower carcass weight, lean percentage, pH decline, and glycolytic potential but have higher fat percentage, water- holding capacity, intramuscular fat content, antioxidant capacity, and percentage of slow-twitch fibers than the Duroc pigs. Moreover, muscles of TB pigs have lower protein synthesis and lipolysis gene expression than the muscles of Duroc pigs. Targeted metabolome analysis indicates that 24 metabolites significantly differ among these three pig breeds. Correlation analysis suggests that L-malic acid and β-alanine contents in muscle are closely related to meat quality. These findings suggest that the excellent meat quality of TB pigs is closely related to muscle metabolism and fiber characteristics, while lower protein synthesis and lipolysis may contribute to less meat yield.