2025-05-30 東京科学大学
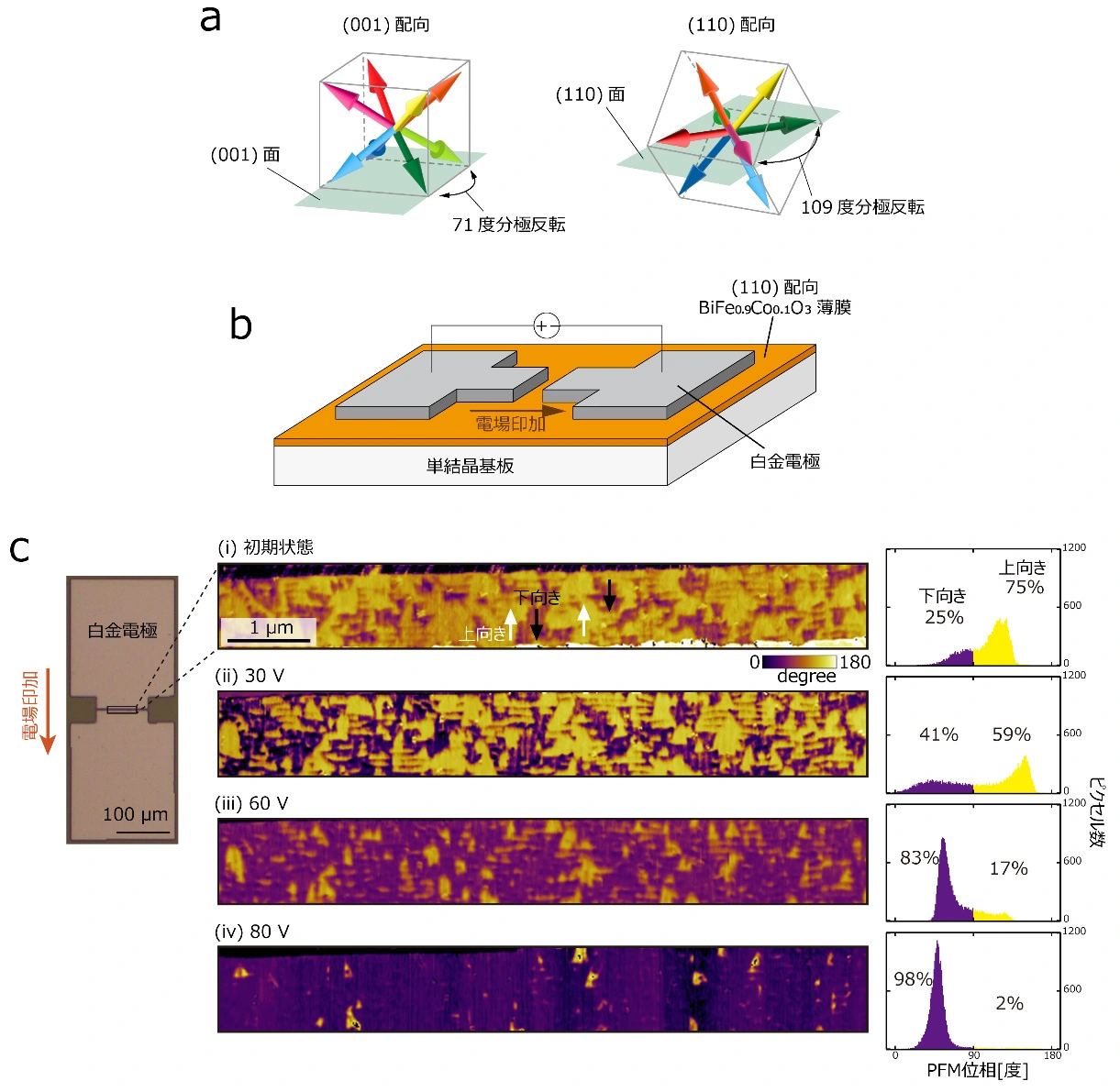 図1. (a)BiFe0.9Co0.1O3の(001)配向と(110)配向の違い。 立方体は結晶構造の最小単位を、8色の矢印は電気分極の取りうる向きを表す。(b)109度分極反転のための白金電極の配置。(c)実際の白金電極の顕微鏡写真と、電場印加による強誘電ドメインの分布の変化(圧電応答顕微鏡図)。黄色と紫色はそれぞれ上向き・下向きの分極を表しており、右図にはその分布のヒストグラムを示している。
図1. (a)BiFe0.9Co0.1O3の(001)配向と(110)配向の違い。 立方体は結晶構造の最小単位を、8色の矢印は電気分極の取りうる向きを表す。(b)109度分極反転のための白金電極の配置。(c)実際の白金電極の顕微鏡写真と、電場印加による強誘電ドメインの分布の変化(圧電応答顕微鏡図)。黄色と紫色はそれぞれ上向き・下向きの分極を表しており、右図にはその分布のヒストグラムを示している。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/xmquit90be64
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1597&prevId=&key=00759a61451f647380adc47261f4d3b5.pdf
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202419580
(110)配向単相マルチフェロイックCo置換BiFeO3薄膜における強磁性の電場駆動反転 Electric-Field-Driven Reversal of Ferromagnetism in (110)-Oriented, Single Phase, Multiferroic Co-Substituted BiFeO3 Thin Films
Takuma Itoh, Kei Shigematsu, Hena Das, Peter Meisenheimer, Kei Maeda, Koomok Lee, Mahir Manna, Surya Prakash Reddy, Sandhya Susarla, Paul Stevenson …
Advanced Materials Published: 28 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202419580
Abstract
While multiferroic materials are attractive systems for the promise of ultra-low-power-consumption computational technologies, electric-field-induced magnetization reversal is a key challenge for realizing devices at scale. Though significant research efforts have been working toward the realization of a material which couples ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism, there are few, even composite, systems which are practical for device scale applications at room temperature. Co-substituted multiferroic BiFe0.9Co0.1O3 is a promising candidate system, due to coupled ferroelectricity and weak ferromagnetism at room temperature. Here, it is theoretically indicated that the ferroic orders in this material are statically coupled, where an in-plane 109° ferroelectric switching event can result in the reversal of this out-of-plane component of magnetization, and the electric field-induced magnetization reversal is experimentally observed. Such an in-plane poling configuration is particularly desirable for device applications.