2025-05-23 北京大学(PKU)
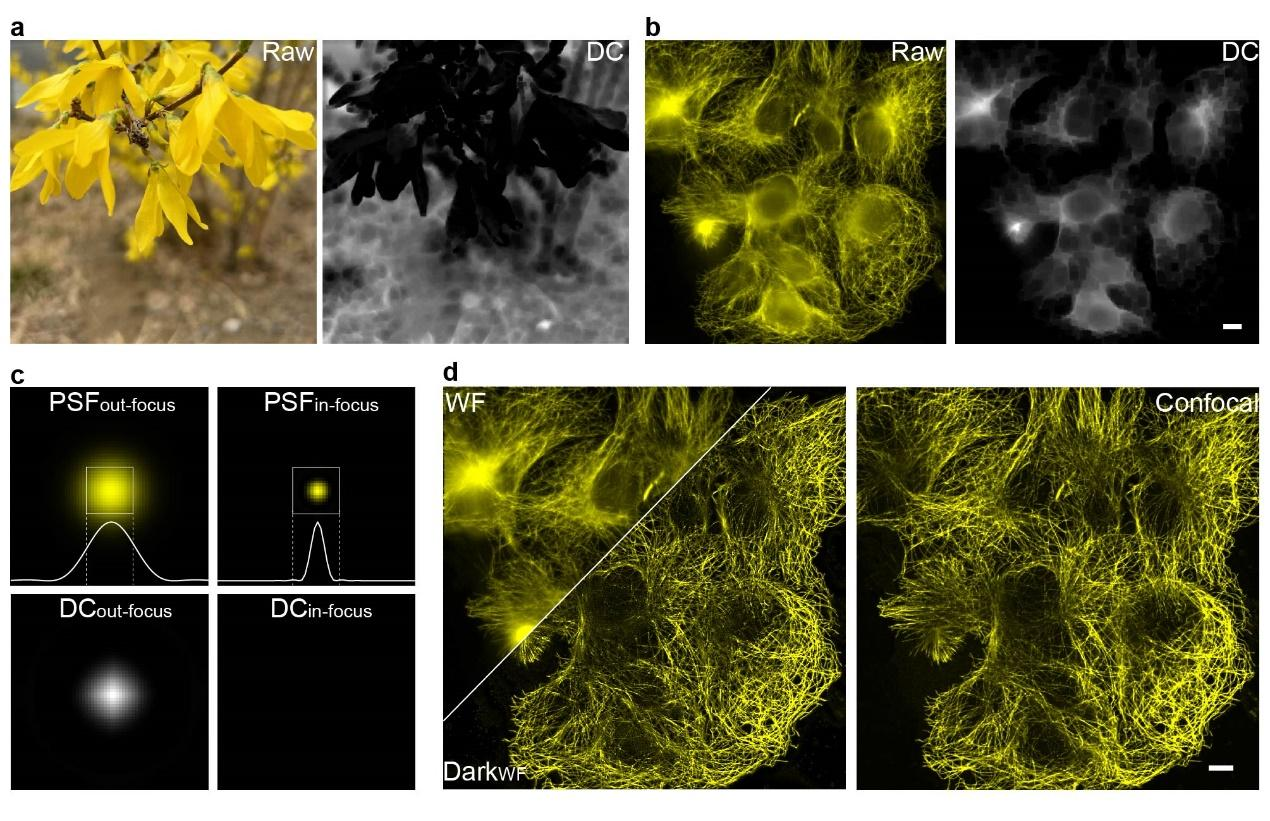
Figure 1. (a, b) Dark channel processing results for natural images and out-of-focus fluorescence images; (c) Differences in dark channel images caused by variations in point spread function (PSF) sizes; (d) Comparison of images before and after Dark sectioning. Scale bar: 4 μm.
<関連情報>
- https://newsen.pku.edu.cn/news_events/news/research/14952.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-025-02667-6
蛍光顕微鏡のバックグラウンド除去を支援する暗黒ベースの光学切片形成 Dark-based optical sectioning assists background removal in fluorescence microscopy
Ruijie Cao,Yaning Li,Yao Zhou,Meiqi Li,Fangrui Lin,Wenyi Wang,Guoxun Zhang,Gang Wang,Boya Jin,Wei Ren,Yu Sun,Zhifeng Zhao,Wei Zhang,Jing Sun,Yiwei Hou,Xinzhu Xu,Jiakui Hu,Wei Shi,Shuang Fu,Qianxi Liang,Yanye Lu,Changhui Li,Yuxuan Zhao,Yiming Li,… Peng Xi
Nature Methods Published:12 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-025-02667-6
Abstract
In fluorescence microscopy, a persistent challenge is the defocused background that obscures cellular details and introduces artifacts. Here, we introduce Dark sectioning, a method inspired by natural image dehazing for removing backgrounds that leverages dark channel prior and dual frequency separation to provide single-frame optical sectioning. Unlike denoising or deconvolution, Dark sectioning specifically targets and removes out-of-focus backgrounds, stably improving the signal-to-background ratio by nearly 10 dB and structural similarity index measure of images by approximately tenfold. Dark sectioning was validated using wide-field, confocal, two/three-dimensional structured illumination and one/two-photon microscopy with high-fidelity reconstruction. We further demonstrate its potential to improve the segmentation accuracy in deep tissues, resulting in better recognition of neurons in the mouse brain and accurate assessment of nuclei in prostate lesions or mouse brain sections. Dark sectioning is compatible with many other microscopy modalities, including light-sheet and light-field microscopy, as well as processing algorithms, including deconvolution and super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging.