2025-04-16 ミシガン大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.umich.edu/advanced-microelectronics-why-a-next-gen-semiconductor-doesnt-fall-to-pieces/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08812-7
ウルツ鉱強誘電体における電界誘起ドメインの壁 Electric-field-induced domain walls in wurtzite ferroelectrics
Ding Wang,Danhao Wang,Mahlet Molla,Yujie Liu,Samuel Yang,Shuaishuai Yuan,Jiangnan Liu,Mingtao Hu,Yuanpeng Wu,Tao Ma,Kai Sun,Hong Guo,Emmanouil Kioupakis & Zetian Mi
Nature Published:16 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08812-7
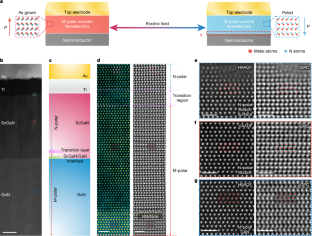
Abstract
Wurtzite ferroelectrics have transformative potential for next-generation microelectronics. A comprehensive understanding of their ferroelectric properties and domain energetics is crucial for tailoring their ferroelectric characteristics and exploiting their functional properties in practical devices. Despite burgeoning interest, the exact configurations and electronic structures of domain walls in wurtzite ferroelectrics remain elusive. Here we explain the atomic configurations and electronic properties of electric-field-induced domain walls in ferroelectric ScGaN. By combining transmission electron microscopy and theoretical calculations, a charged domain wall with a buckled two-dimensional hexagonal phase is revealed. Density functional theory calculations confirm that such domain-wall structures further give rise to unprecedented mid-gap states within the forbidden band. Quantitative analysis unveils a universal charge-compensation mechanism stabilizing antipolar domain walls in ferroelectric materials, in which the polarization discontinuity at the 180° domain wall is compensated by the unbonded valence electrons. Furthermore, the reconfigurable conductivity of these domain walls is experimentally demonstrated, showcasing their potential for ultrascaled device applications.