2025-03-21 日本原子力研究開発機構,筑波大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.jaea.go.jp/02/press2024/p25032102/
- https://pubs.aip.org/aip/pof/article/37/3/033333/3339139/Atomization-mechanisms-in-the-vortex-like-flow-of
浅いプール内の壁面衝突噴流の渦状流における微粒化機構
Atomization mechanisms in the vortex-like flow of a wall-impinging jet in a shallow pool
Naoki Horiguchi (堀口直樹);Hiroyuki Yoshida (吉田啓之);Akiko Kaneko (金子暁子);Yutaka Abe (阿部豊)
Physics of Fluids Published:March 10 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0253743
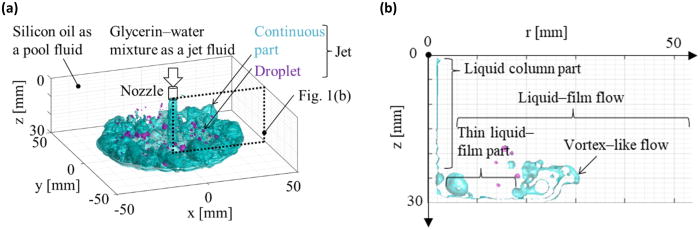
This study aimed to reveal the atomization mechanisms in the vortex-like flow of a wall-impinging jet in a shallow pool of a liquid–liquid system, focusing on droplet formation as an elementary process of atomization. To quantitatively investigate these mechanisms, we applied quantification methods to three-dimensional interfacial data obtained by a previous experimental study using three-dimensional laser-induced fluorescence with index matching. Detailed observations of the spreading behavior of droplets and vortex-like flow, along with quantitative estimations, found out that the vortex-like flow is the dominant source of droplets on the atomization. Furthermore, investigations into the forces acting on the vortex-like flow found out the formation and collapse processes of the vortex-like flow. The accelerations of the normal forces can be represented by superficial centrifugal acceleration and gravitational acceleration. Our next analysis focused on investigating droplet formation as the elementary process of atomization. The results showed two droplet formation patterns: liquid-film breaking patterns, wherein droplets directly form from the liquid film, and the surfing pattern, wherein droplets form from interfacial waves on the liquid film. Subsequently, the droplet data, grouped using dimensionless numbers, were compared with theoretical lines describing the different droplet formation mechanisms. This comparison revealed the mechanisms of droplet formation within the vortex-like flow.