2025-01-20 ミシガン大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.umich.edu/new-water-purification-technology-helps-turn-seawater-into-drinking-water-without-tons-of-chemicals/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s44221-024-00362-y
ホウ素除去における高選択的かつエネルギー効率の高いアプローチが海水淡水化のアキレス腱を克服する A highly selective and energy efficient approach to boron removal overcomes the Achilles heel of seawater desalination
Weiyi Pan,Debashis Roy,Betül Uralcan,Sohum K. Patel,Arpita Iddya,Eungjin Ahn,Amir Haji-Akbari,Jovan Kamcev & Menachem Elimelech
Nature Water Published:20 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s44221-024-00362-y
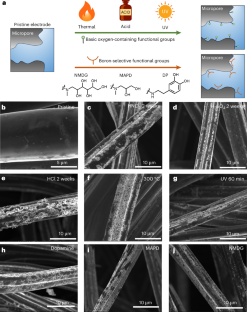
Abstract
Selective removal of trace contaminants from water remains a crucial challenge in water treatment. Boron is a trace contaminant that is ubiquitous in seawater and has been widely detected in groundwater. Current boron removal methods, such as multi-stage reverse osmosis and ion-exchange adsorption, are chemical and energy intensive, necessitating the development of more sustainable technologies. Here we address this challenge by developing surface functionalized microporous electrodes that enable boron-selective bipolar membrane-assisted electrosorption. Our study demonstrates that micropore functionalization with oxygen-containing (hydroxyl, lactone and carboxyl) and boron-selective (dopamine, 3-methylamino-1,2-propanediol and N-methyl-d-glucamine) functional groups substantially improves electrode performance for boron removal and selectivity. The functionalized electrodes exhibit a boron removal selectivity that is an order of magnitude higher than that of the pristine electrode, facilitating energy efficient boron electrosorption. We identify hydroxyl groups as the key factor in enhancing boron removal performance and selectivity during electrosorption. Molecular dynamics simulations demonstrate the underlying mechanisms of boron selectivity, highlighting the role of hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups and boron in governing the boron-selective electrosorption process.