2023-03-13 ローレンスリバモア国立研究所(LLNL)
この新技術は、農業排水から硝酸塩を取り除き、肥料に変えることができ、廃棄物処理、持続可能な化学生産、そして脱炭素化の推進に影響を与えることが期待されている。今後は、より選択的な材料を使用してさらなる改良を行い、大規模なシステムの開発を目指す予定である。
<関連情報>
- https://www.llnl.gov/news/demonstrating-energy-efficient-conversion-nitrate-pollutants-ammonia
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-36318-1
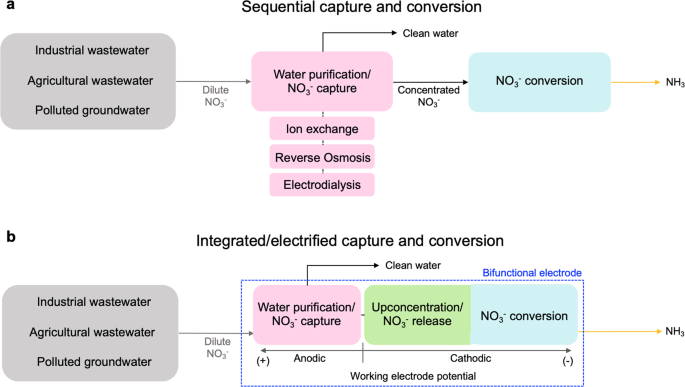
二重機能性レドックス電極を用いた硝酸塩の回収とアンモニア製造のカップリング Coupling nitrate capture with ammonia production through bifunctional redox-electrodes
Kwiyong Kim,Alexandra Zagalskaya,Jing Lian Ng,Jaeyoung Hong,Vitaly Alexandrov,Tuan Anh Pham & Xiao Su
Nature Communications Published:14 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36318-1
Abstract
Nitrate is a ubiquitous aqueous pollutant from agricultural and industrial activities. At the same time, conversion of nitrate to ammonia provides an attractive solution for the coupled environmental and energy challenge underlying the nitrogen cycle, by valorizing a pollutant to a carbon-free energy carrier and essential chemical feedstock. Mass transport limitations are a key obstacle to the efficient conversion of nitrate to ammonia from water streams, due to the dilute concentration of nitrate. Here, we develop bifunctional electrodes that couple a nitrate-selective redox-electrosorbent (polyaniline) with an electrocatalyst (cobalt oxide) for nitrate to ammonium conversion. We demonstrate the synergistic reactive separation of nitrate through solely electrochemical control. Electrochemically-reversible nitrate uptake greater than 70 mg/g can be achieved, with electronic structure calculations and spectroscopic measurements providing insight into the underlying role of hydrogen bonding for nitrate selectivity. Using agricultural tile drainage water containing dilute nitrate (0.27 mM), we demonstrate that the bifunctional electrode can achieve a 8-fold up-concentration of nitrate, a 24-fold enhancement of ammonium production rate (108.1 ug h−1 cm−2), and a >10-fold enhancement in energy efficiency when compared to direct electrocatalysis in the dilute stream. Our study provides a generalized strategy for a fully electrified reaction-separation pathway for modular nitrate remediation and ammonia production.