2024-08-02 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
カブトムシと羽ばたきマイクロロボットの受動的な翼の展開と後退 Passive wing deployment and retraction in beetles and flapping microrobots
Hoang-Vu ,Hoon Cheol Park & Dario Floreano
Nature Published:31 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07755-9
Abstract
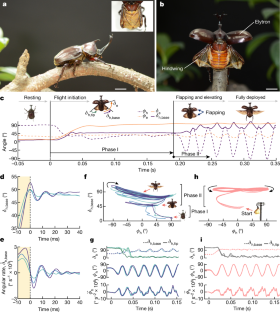
Birds, bats and many insects can tuck their wings against their bodies when at rest and deploy them to power flight. Whereas birds and bats use well-developed pectoral and wing muscles1,2, how insects control their wing deployment and retraction remains unclear because this varies among insect species. Beetles (Coleoptera) display one of the most complex mechanisms. In rhinoceros beetles, Allomyrina dichotoma, wing deployment is initiated by complete release of the elytra and partial release of the hindwings at their bases. Subsequently, the beetle starts flapping, elevates the hindwing bases and unfolds the hindwing tips in an origami-like fashion. Although the origami-like fold has been extensively explored3,4,5,6,7,8, limited attention has been given to the hindwing base movements, which are believed to be driven by the thoracic muscles5,9,10,11. Here we demonstrate that rhinoceros beetles can effortlessly deploy their hindwings without necessitating muscular activity. We show that opening the elytra triggers a spring-like partial release of the hindwings from the body, allowing the clearance needed for the subsequent flapping motion that brings the hindwings into the flight position. After flight, the beetle can use the elytra to push the hindwings back into the resting position, further strengthening the hypothesis of passive deployment. We validated the hypothesis using a flapping microrobot that passively deployed its wings for stable, controlled flight and retracted them neatly upon landing, demonstrating a simple, yet effective, approach to the design of insect-like flying micromachines.



