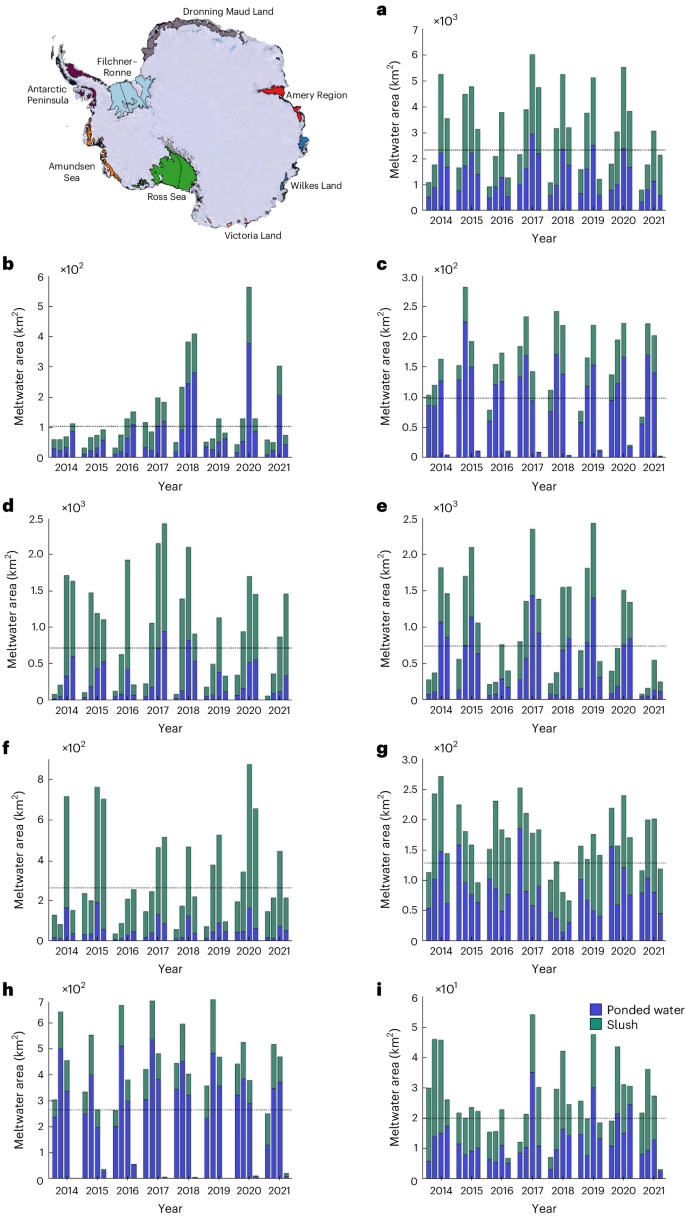
2024-06-27 カリフォルニア大学サンタバーバラ校(UCSB)
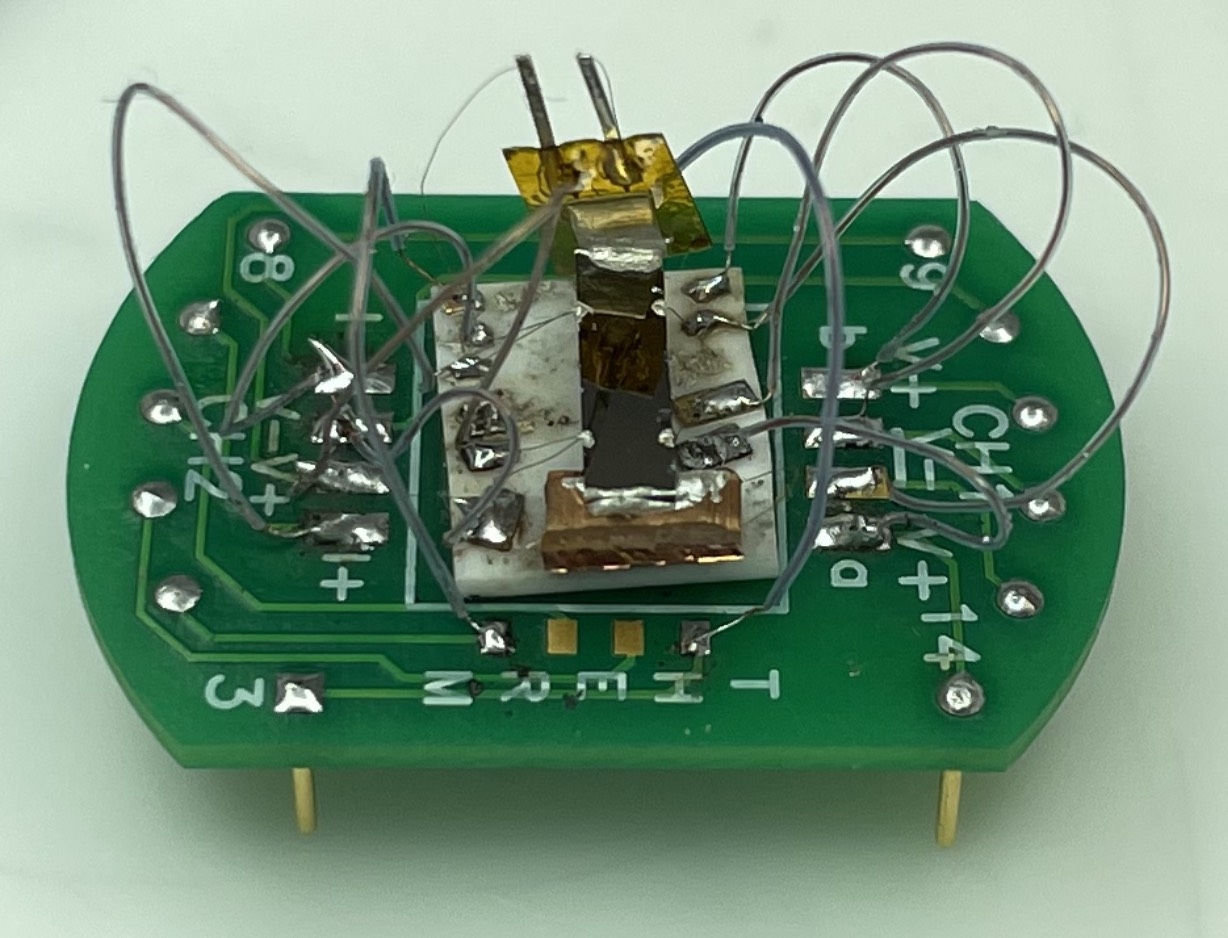
Photo Credit
Courtesy Image
This device tests the properties of the cadmium arsenide thin film — the black strip in the center
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucsb.edu/2024/021535/investigating-extraordinary-thermoelectric-properties-cadmium-arsenide-thin-films
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202311644
量子閉じ込めCd3As2薄膜におけるトポロジカル表面状態の特異な熱電特性 Extraordinary Thermoelectric Properties of Topological Surface States in Quantum-Confined Cd3As2 Thin Films
Wenkai Ouyang, Alexander C. Lygo, Yubi Chen, Huiyuan Zheng, Dung Vu, Brandi L. Wooten, Xichen Liang, Joseph P. Heremans, Susanne Stemmer, Bolin Liao
Advanced Materials Published: 29 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202311644
Abstract
Topological insulators and semimetals have been shown to possess intriguing thermoelectric properties promising for energy harvesting and cooling applications. However, thermoelectric transport associated with the Fermi arc topological surface states on topological Dirac semimetals remains less explored. This work systematically examines thermoelectric transport in a series of topological Dirac semimetal Cd3As2 thin films grown by molecular beam epitaxy. Surprisingly, significantly enhanced Seebeck effect and anomalous Nernst effect are found at cryogenic temperatures when the Cd3As2 layer is thin. In particular, a peak Seebeck coefficient of nearly 500 µV K−1 and a corresponding thermoelectric power factor over 30 mW K−2 m−1 are observed at 5 K in a 25-nm-thick sample. Combining angle-dependent quantum oscillation analysis, magnetothermoelectric measurement, transport modeling, and first-principles simulation, the contributions from bulk and surface conducting channels are isolated and the unusual thermoelectric properties are attributed to the topological surface states. The analysis showcases the rich thermoelectric transport physics in quantum-confined topological Dirac semimetal thin films and suggests new routes to achieving high thermoelectric performance at cryogenic temperatures.