2024-05-24 バージニア工科大学(VirginiaTech)
<関連情報>
- https://news.vt.edu/articles/2024/05/eng-me-cheng-leidenfrost-limits-nature-physics.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-024-02522-z
微小構造表面上の無柄な液滴の低温ライデンフロスト様ジャンピング Low-temperature Leidenfrost-like jumping of sessile droplets on microstructured surfaces
Wenge Huang,Lei Zhao,Xukun He,Yang Li,C. Patrick Collier,Zheng Zheng,Jiansheng Liu,Dayrl P. Briggs & Jiangtao Cheng
Nature Physics Published:24 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-024-02522-z
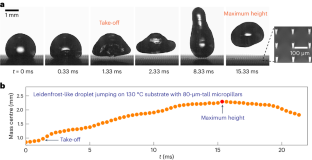
Abstract
The Leidenfrost effect—the levitation and hovering of liquid droplets on hot solid surfaces—generally requires a sufficiently high substrate temperature to activate liquid vaporization. Here we report the modulation of Leidenfrost-like jumping of sessile water microdroplets on micropillared surfaces at a relatively low temperature. Compared to traditional Leidenfrost effect occurring above 230 °C, the fin-array-like micropillars enable water microdroplets to levitate and jump off the surface within milliseconds at a temperature of 130 °C by triggering the inertia-controlled growth of individual vapour bubbles at the droplet base. We demonstrate that droplet jumping, resulting from momentum interactions between the expanding vapour bubble and the droplet, can be modulated by tailoring of the thermal boundary layer thickness through pillar height. This enables regulation of the bubble expansion between the inertia-controlled mode and the heat-transfer-limited mode. The two bubble-growth modes give rise to distinct droplet jumping behaviours characterized by constant velocity and constant energy regimes, respectively. This heating strategy allows the straightforward purging of wetting liquid droplets on rough or structured surfaces in a controlled manner, with potential applications including the rapid removal of fouling media, even when located in surface cavities.