2024-04-08 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/researchers-unveil-the-largest-3d-map-of-the-unive/
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.06313
DESI 1パーセントサーベイ: UNITシミュレーションによる複数のトレーサーに対する一般化されたSHAMの探索 The DESI One-Percent Survey: Exploring A Generalized SHAM for Multiple Tracers with the UNIT Simulation
Jiaxi Yu, Cheng Zhao, Violeta Gonzalez-Perez, Chia-Hsun Chuang, Allyson Brodzeller, Arnaud de Mattia, Jean-Paul Kneib, Alex Krolewski, Antoine Rocher, Ashley Ross, Yunchong Wang, Sihan Yuan, Hanyu Zhang, Rongpu Zhou, Jessica Nicole Aguilar, Steven Ahlen, David Brooks, Kyle Dawson, Alex de la Macorra, Peter Doel, Kevin Fanning, Andreu Font-Ribera, Jaime Forero-Romero, Satya Gontcho A Gontcho, Klaus Honscheid, Robert Kehoe, Theodore Kisner, Anthony Kremin, Martin Landriau, Marc Manera, Paul Martini, Aaron Meisner, Ramon Miquel, John Moustakas, Jundan Nie, Will Percival, Claire Poppett, Anand Raichoor, Graziano Rossi, Hee-Jong Seo, Gregory Tarlé, Zhimin Zhou, Hu Zou
arXiv last revised 14 Nov 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2306.06313
Abstract
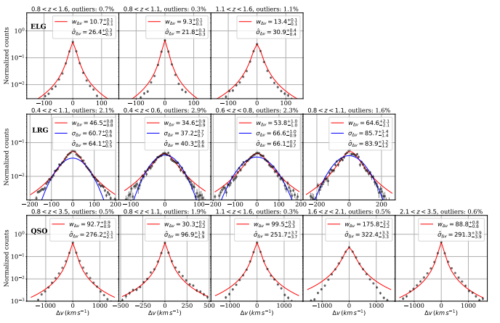
We perform SubHalo Abundance Matching (SHAM) studies on UNIT simulations with \{σ,Vceil,υsmear\}-SHAM and \{σ,Vceil,ƒsat\}-SHAM. They are designed to reproduce the clustering on 5–30$\,\hmpc$ of Luminous Red Galaxies (LRGs), Emission Line Galaxies (ELGs) and Quasi-Stellar Objects (QSOs) at 0.4<z<3.5 from DESI One Percent Survey. Vceil is the incompleteness of the massive host (sub)haloes and is the key to the generalized SHAM. υsmear models the clustering effect of redshift uncertainties, providing measurments consistent with those from repeat observations. A free satellite fraction ƒsat is necessary to reproduce the clustering of ELGs. We find ELGs present a more complex galaxy–halo mass relation than LRGs reflected in their weak constraints on σ. LRGs, QSOs and ELGs show increasing Vceil values, corresponding to the massive galaxy incompleteness of LRGs, the quenched star formation of ELGs and the quenched black hole accretion of QSOs. For LRGs, a Gaussian υsmear presents a better profile for sub-samples at redshift bins than a Lorentzian profile used for other tracers. The impact of the statistical redshift uncertainty on ELG clustering is negligible. The best-fitting satellite fraction for DESI ELGs is around 4 per cent, lower than previous estimations for ELGs. The mean halo mass log10(⟨Mvir⟩) in $\Msun{}$ for LRGs, ELGs and QSOs are 13.16±0.01, 11.90±0.06 and 12.66±0.45 respectively. Our generalized SHAM algorithms facilitate the production of mult-tracer galaxy mocks for cosmological tests.