2024-04-03 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
◆UNFOLDの研究者らは、センサー技術と機械学習の組み合わせによってVAWTの効率を200%向上させ、振動を77%減少させることができる最適なピッチプロファイルを特定した。これにより、VAWTの欠点である風の変動に対する抵抗力を強化し、効率的で信頼性の高いVAWT技術を商業化する可能性が高まった。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/machine-learning-enables-viability-of-vertical-a-2/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46988-0
垂直軸風力タービンの性能向上のための最適ブレードピッチ制御 Optimal blade pitch control for enhanced vertical-axis wind turbine performance
Sébastien Le Fouest & Karen Mulleners
Nature Communications Published:30 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46988-0
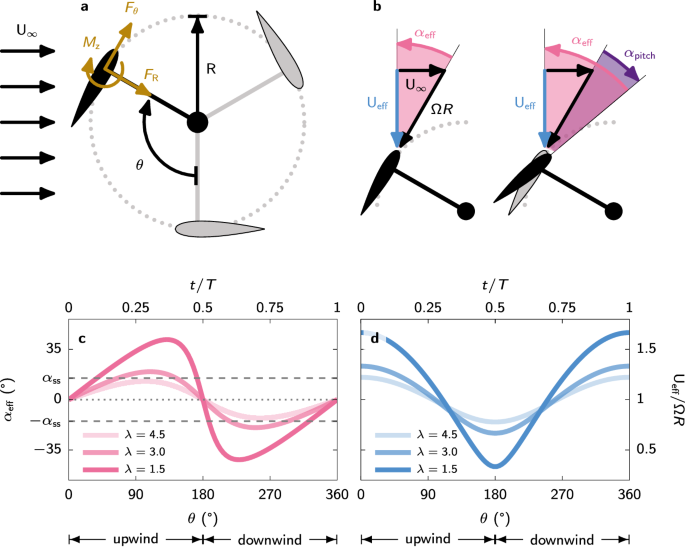
Abstract
Vertical-axis wind turbines are great candidates to enable wind power extraction in urban and off-shore applications. Currently, concerns around turbine efficiency and structural integrity limit their industrial deployment. Flow control can mitigate these concerns. Here, we experimentally demonstrate the potential of individual blade pitching as a control strategy and explain the flow physics that yields the performance enhancement. We perform automated experiments using a scaled-down turbine model coupled to a genetic algorithm optimiser to identify optimal pitching kinematics at on- and off-design operating conditions. We obtain two sets of optimal pitch profiles that achieve a three-fold increase in power coefficient at both operating conditions compared to the non-actuated turbine and a 77% reduction in structure-threatening load fluctuations at off-design conditions. Based on flow field measurements, we uncover how blade pitching manipulates the flow structures to enhance performance. Our results can aid vertical-axis wind turbines increase their much-needed contribution to our energy needs.