2024-03-25 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-024-01460-w
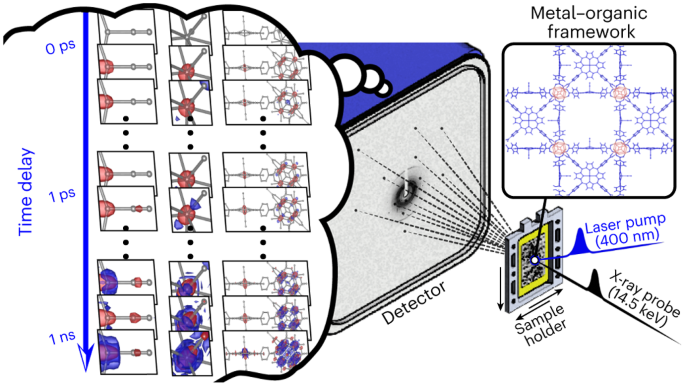
フェムト秒連続結晶構造解析で捉えた有機金属骨格のダイナミックな3次元構造 Dynamic three-dimensional structures of a metal–organic framework captured with femtosecond serial crystallography
Jaedong Kang,Yunbeom Lee,Seonggon Lee,Hosung Ki,Jungmin Kim,Jain Gu,Yongjun Cha,Jun Heo,Kyung Won Lee,Seong Ok Kim,Jaehyun Park,Sang-Youn Park,Sangsoo Kim,Rory Ma,Intae Eom,Minseok Kim,Jeongho Kim,Jae Hyuk Lee & Hyotcherl Ihee
Nature Chemistry Published:25 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-024-01460-w
Abstract
Crystalline systems consisting of small-molecule building blocks have emerged as promising materials with diverse applications. It is of great importance to characterize not only their static structures but also the conversion of their structures in response to external stimuli. Femtosecond time-resolved crystallography has the potential to probe the real-time dynamics of structural transitions, but, thus far, this has not been realized for chemical reactions in non-biological crystals. In this study, we applied time-resolved serial femtosecond crystallography (TR-SFX), a powerful technique for visualizing protein structural dynamics, to a metal–organic framework, consisting of Fe porphyrins and hexazirconium nodes, and elucidated its structural dynamics. The time-resolved electron density maps derived from the TR-SFX data unveil trifurcating structural pathways: coherent oscillatory movements of Zr and Fe atoms, a transient structure with the Fe porphyrins and Zr6 nodes undergoing doming and disordering movements, respectively, and a vibrationally hot structure with isotropic structural disorder. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of using TR-SFX to study chemical systems.