2024-01-16 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
◆PNNLの科学者が開発し、自動化と機械学習を組み合わせたLipidOzは、既存手法の制約を克服し、脂質の特性を効率的かつ正確に特定することが可能です。このツールはガス相酸化反応(OzID)を使用し、標準的な脂質混合物や複雑な脂質エキスに対する将来のリピドミクス研究に実用的なアプローチを提供します。
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/publications/lipidoz-new-software-enables-identification-lipid-double-bond-locations
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42004-023-00867-9
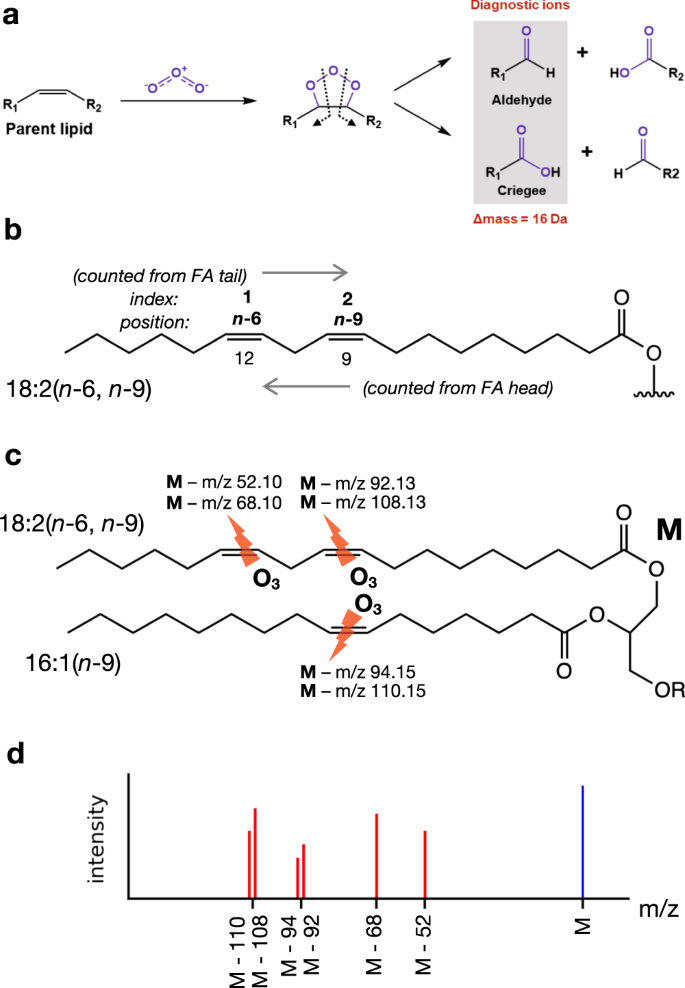
LipidOz、オゾン誘起解離質量分析データから脂質の炭素-炭素二重結合の位置を自動で解明可能に LipidOz enables automated elucidation of lipid carbon–carbon double bond positions from ozone-induced dissociation mass spectrometry data
Dylan H. Ross,Joon-Yong Lee,Aivett Bilbao,Daniel J. Orton,Josie G. Eder,Meagan C. Burnet,Brooke L. Deatherage Kaiser,Jennifer E. Kyle & Xueyun Zheng
Communications Chemistry Published:19 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-023-00867-9
Abstract
Lipids play essential roles in many biological processes and disease pathology, but unambiguous identification of lipids is complicated by the presence of multiple isomeric species differing by fatty acyl chain length, stereospecifically numbered (sn) position, and position/stereochemistry of double bonds. Conventional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses enable the determination of fatty acyl chain lengths (and in some cases sn position) and number of double bonds, but not carbon-carbon double bond positions. Ozone-induced dissociation (OzID) is a gas-phase oxidation reaction that produces characteristic fragments from lipids containing double bonds. OzID can be incorporated into ion mobility spectrometry (IMS)-MS instruments for the structural characterization of lipids, including additional isomer separation and confident assignment of double bond positions. The complexity and repetitive nature of OzID data analysis and lack of software tool support have limited the application of OzID for routine lipidomics studies. Here, we present an open-source Python tool, LipidOz, for the automated determination of lipid double bond positions from OzID-IMS-MS data, which employs a combination of traditional automation and deep learning approaches. Our results demonstrate the ability of LipidOz to robustly assign double bond positions for lipid standard mixtures and complex lipid extracts, enabling practical application of OzID for future lipidomics.