2023-09-12 サンディア国立研究所(SNL)
◆このインクは、従来のインクとは異なり、複雑な署名で難しい偽造や逆算を防ぎます。この技術を活用することで、合法的な企業は詐欺師に先んじて消費者の安全を確保できる可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://newsreleases.sandia.gov/invisible_inks/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-36576-z
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsami.1c24477
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.202013012
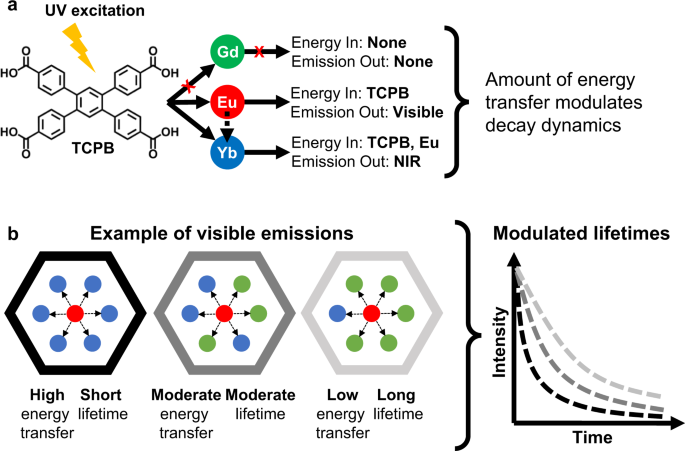
ヘテロ金属希土類MOFにおける金属間エネルギー移動による直交発光寿命エンコーディング Orthogonal luminescence lifetime encoding by intermetallic energy transfer in heterometallic rare-earth MOFs
Jacob I. Deneff,Lauren E. S. Rohwer,Kimberly S. Butler,Bryan Kaehr,Dayton J. Vogel,Ting S. Luk,Raphael A. Reyes,Alvaro A. Cruz-Cabrera,James E. Martin & Dorina F. Sava Gallis
Nature Communications Published:22 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36576-z
Abstract
Lifetime-encoded materials are particularly attractive as optical tags, however examples are rare and hindered in practical application by complex interrogation methods. Here, we demonstrate a design strategy towards multiplexed, lifetime-encoded tags via engineering intermetallic energy transfer in a family of heterometallic rare-earth metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). The MOFs are derived from a combination of a high-energy donor (Eu), a low-energy acceptor (Yb) and an optically inactive ion (Gd) with the 1,2,4,5 tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl) benzene (TCPB) organic linker. Precise manipulation of the luminescence decay dynamics over a wide microsecond regime is achieved via control over metal distribution in these systems. Demonstration of this platform’s relevance as a tag is attained via a dynamic double encoding method that uses the braille alphabet, and by incorporation into photocurable inks patterned on glass and interrogated via digital high-speed imaging. This study reveals true orthogonality in encoding using independently variable lifetime and composition, and highlights the utility of this design strategy, combining facile synthesis and interrogation with complex optical properties.
混合クラスター型ヘテロ金属MOFにおけるDNA-フルオロフォア会合によるプログラム可能なフォトルミネッセンス Programmable Photoluminescence via Intrinsic and DNA–Fluorophore Association in a Mixed Cluster Heterometallic MOF
Dorina F. Sava Gallis, Kimberly S. Butler, Charles J. Pearce, Nichole Valdez, and Mark A. Rodriguez
ACS Applied Materialus & Interfaces Published:February 16, 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c24477
Abstract

A rapid and facile design strategy to create a highly complex optical tag with programmable, multimodal photoluminescent properties is described. This was achieved via intrinsic and DNA–fluorophore hidden signatures. As a first covert feature of the tag, an intricate novel heterometallic near-infrared (NIR)-emitting mesoporous metal–organic framework (MOF) was designed and synthesized. The material is constructed from two chemically distinct, homometallic hexanuclear clusters based on Nd and Yb. Uniquely, the Nd-based cluster is observed here for the first time in a MOF and consists of two staggered Nd μ3-oxo trimers. To generate controlled, multimodal, and tailorable emission with difficult to counterfeit features, the NIR-emissive MOF was post-synthetically modified via a fluorescent DNA oligo labeling design strategy. The surface attachment of several distinct fluorophores, including the simultaneous attachment of up to three distinct fluorescently labeled oligos was achieved, with excitation and emission properties across the visible spectrum (480–800 nm). The DNA inclusion as a secondary covert element in the tag was demonstrated via the detection of SYBR Gold dye association. Importantly, the approach implemented here serves as a rapid and tailorable way to encrypt distinct information in a facile and modular fashion and provides an innovative technology in the quest toward complex optical tags.
偽造防止用ヘテロ金属MOFベース光タグにおける多層複雑性の符号化 Encoding Multilayer Complexity in Anti-Counterfeiting Heterometallic MOF-Based Optical Tags
Jacob I. Deneff, Kimberly S. Butler, Lauren E. S. Rohwer, Charles J. Pearce, Nichole R. Valdez, Mark A. Rodriguez, Ting S. Luk, Dorina F. Sava Gallis
Angewandte Chemie International Edition Published: 02 November 2020
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202013012
Graphical Abstract
To increase complexity and security in optical tags, heterometallic rare-earth metal–organic frameworks with both overt (visible) and covert (near-infrared) properties were targeted. Multilayer intricacy is imparted by concomitant multi-emissive spectra and highly tunable luminescence lifetimes. Intermetal charge transfer in these systems results in difficult-to-counterfeit optical tags with unique photophysical properties.
Abstract
Optical tags provide a way to quickly and unambiguously identify valuable assets. Current tag fluorophore options lack the tunability to allow combined methods of encoding in a single material. Herein we report a design strategy to encode multilayer complexity in a family of heterometallic rare-earth metal–organic frameworks based on highly connected nonanuclear clusters. To impart both intricacy and security, a synergistic approach was implemented resulting in both overt (visible) and covert (near-infrared, NIR) properties, with concomitant multi-emissive spectra and tunable luminescence lifetimes. Tag authentication is validated with a variety of orthogonal detection methodologies. Importantly, the effect induced by subtle compositional changes on intermetallic energy transfer, and thus on the resulting photophysical properties, is demonstrated. This strategy can be widely implemented to create a large library of highly complex, difficult-to-counterfeit optical tags.