2023-08-11 韓国基礎科学研究院(IBS)
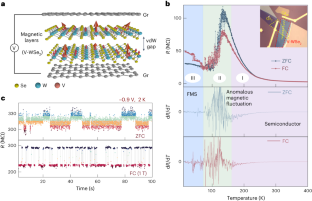
◆彼らは、バナジウムをタングステン二硒化物(V-WSe2)に微小な磁性ドーパントとして導入することで、vdWレイヤーセミコンダクターで磁性の変動と巨大なRTN信号を生成できる可能性があることを報告しました。この新技術は、スピントロニクスにおいて磁気スイッチング能力を提供する可能性を秘めています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ibs.re.kr/cop/bbs/BBSMSTR_000000000738/selectBoardArticle.do
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-023-01002-1
多層バナジウムドープ二セレン化タングステンにおける電気的可変磁気ゆらぎ Electrically tunable magnetic fluctuations in multilayered vanadium-doped tungsten diselenide
Lan-Anh T. Nguyen,Jinbao Jiang,Tuan Dung Nguyen,Philip Kim,Min-Kyu Joo,Dinh Loc Duong & Young Hee Lee
Nature Electronics Published:10 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-023-01002-1
Abstract
Fluctuations are ubiquitous in magnetic materials and can cause random telegraph noise. Such noise is of potential use in systems such as spiking neuron devices, random number generators and probability bits. Here we report electrically tunable magnetic fluctuations and random telegraph noise in multilayered vanadium-doped tungsten diselenide (WSe2) using vertical tunnelling heterostructure devices composed of graphene/vanadium-doped WSe2/graphene and magnetoresistance measurements. We identify bistable magnetic states through discrete Gaussian peaks in the random telegraph noise histogram and the 1/f2 features of the noise power spectrum. Three categories of fluctuation are detected: small resistance fluctuations at high temperatures due to intralayer coupling between the magnetic domains; large resistance changes over a wide range of temperatures; and persistent large resistance changes at low temperatures due to magnetic interlayer coupling. We also show that the bistable state and cut-off frequency of the random telegraph noise can be modulated with an electric bias.