この研究結果は、カリフォルニア州の地震災害の評価に重要な示唆を与える可能性がある。 The findings could have important takeaways for assessing seismic hazards in California
2023-08-03 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
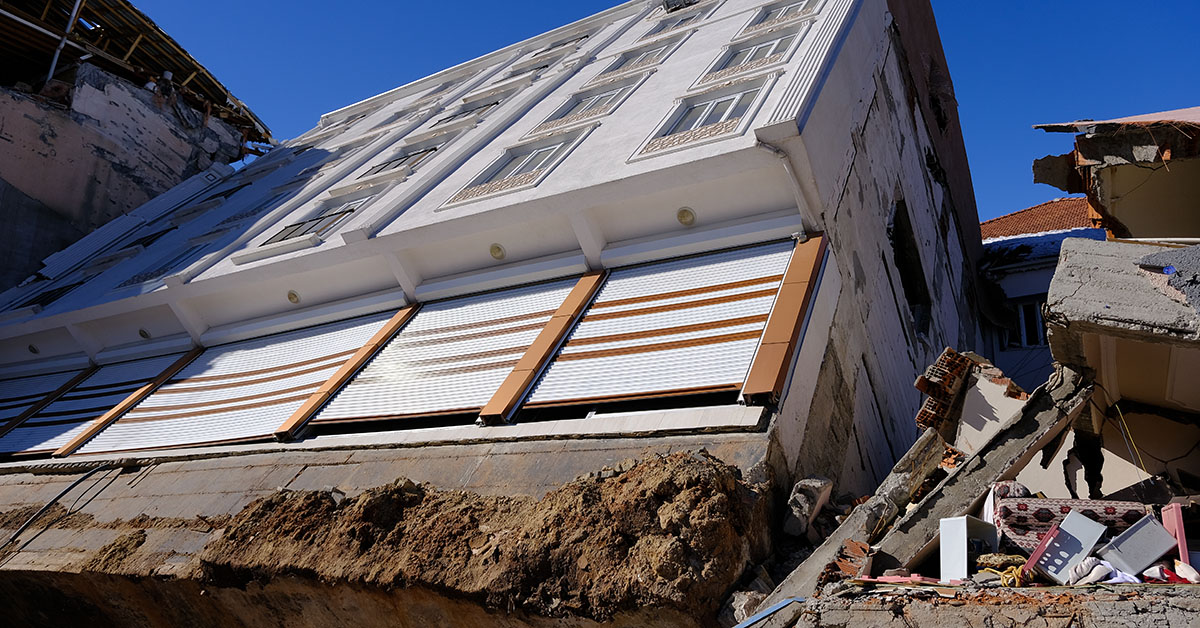

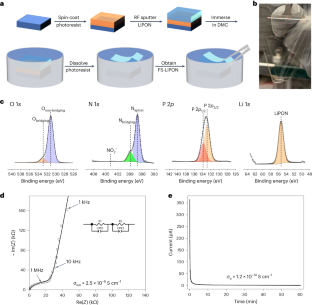
Due to ground liquefaction during the Turkey-Syria quake, this building broke from the foundation and fell on the building behind it. Photo: Mahmut Sonmez/iStock
◆一つ目の地震は断層の曲げや結合点を通過し、予想外の「カスケード」が強度を増し、二つ目の地震は予期せぬ「超音速断層破壊」が発生し、揺れを増幅させました。
◆この研究はトルコ周辺の地震活動の理解を深め、サンアンドレアス断層地帯にも応用できる重要な知見を提供しています。
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/the-unexpected-physics-behind-turkeys-devastating-2023-earthquakes
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adi0685
2023年トルコ・カフラマンマラシュ地震(Mw7.8-7.7)の複雑なダイナミクス The complex dynamics of the 2023 Kahramanmaraş, Turkey, Mw 7.8-7.7 earthquake doublet
Zhe Jia,Zeyu Jin,Mathilde Marchandon,Thomas Ulrich,Alice-Agnes Gabriel,Wenyuan Fan,Peter Shearer,Xiaoyu Zou,John Rekoske,Fatih Bulut,Asli Garagon, and Yuri Fialko
Science Published:3 Aug 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adi0685
Abstract
The destructive 2023 moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8-7.7 earthquake doublet ruptured multiple segments of the East Anatolian Fault system in Turkey. We integrate multi-scale seismic and space-geodetic observations with multi-fault kinematic inversions and dynamic rupture modeling to unravel the events’ complex rupture history and stress-mediated fault interactions. Our analysis reveals three sub-shear slip episodes during the initial Mw 7.8 earthquake with delayed rupture initiation to the southwest. The Mw 7.7 event occurred 9 hours later with larger slip and supershear rupture on its western branch. Mechanically consistent dynamic models accounting for fault interactions can explain the unexpected rupture paths, and require a heterogeneous background stress. Our results highlight the importance of combining near- and far-field observations with data-driven and physics-based models for seismic hazard assessment.