2023-07-18 米国国立再生可能エネルギー研究所(NREL)
◆特に、新しい手法は研究室以外でも再現可能であり、より速いEV充電の実現に向けた大きな進展です。この研究は、オープンなデータ共有と国立研究所の協力の重要性を示す素晴らしい例です。さらに、新しいモデルにより、リチウムプレートの挙動をシミュレートして不可逆的なリチウム消費を回避することが可能になります。この研究は、リチウムイオン電池をより効率的で持続可能なエネルギー源に進化させるための重要な一歩とされています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.nrel.gov/news/program/2023/full-speed-ahead-modeling-faster-future-lithium-ion-batteries.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-023-01194-y
高速充電電池設計のための高スループットLiめっき定量化 High-throughput Li plating quantification for fast-charging battery design
Zachary M. Konz,Brendan M. Wirtz,Ankit Verma,Tzu-Yang Huang,Helen K. Bergstrom,Matthew J. Crafton,David E. Brown,Eric J. McShane,Andrew M. Colclasure & Bryan D. McCloskey
Nature Energy Published:02 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-023-01194-y
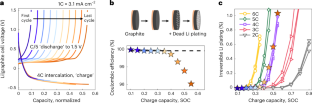
Abstract
Fast charging of most commercial lithium-ion batteries is limited due to fear of lithium plating on the graphite anode, which is difficult to detect and poses considerable safety risk. Here we demonstrate the power of simple, accessible and high-throughput cycling techniques to quantify irreversible Li plating spanning data from over 200 cells. We first observe the effects of energy density, charge rate, temperature and state of charge on lithium plating, use the results to refine a mature physics-based electrochemical model and provide an interpretable empirical equation for predicting the plating onset state of charge. We then explore the reversibility of lithium plating and its connection to electrolyte design for preventing irreversible Li accumulation. Finally, we design a method to quantify in situ Li plating for commercially relevant graphite|LiNi0.5Mn0.3Co0.2O2 (NMC) cells and compare with results from the experimentally convenient Li|graphite configuration. The hypotheses and abundant data herein were generated primarily with equipment universal to the battery researcher, encouraging further development of innovative testing methods and data processing that enable rapid battery engineering.



