2023-05-25 ノースカロライナ州立大学(NCState)
◆研究結果は、繊維を異なる目的に合わせる上での指針となる可能性があります。これらの繊維は、生体内の3Dモデルの開発にも利用できるかもしれません。研究者たちは、細胞の動きや伸縮に対する応答を調査し、機械的なストレスが細胞の分化にどのような影響を与えるかをさらに研究する予定です。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ncsu.edu/2023/05/artificial-muscle-fibers-could-serve-as-cell-scaffolds/
- https://www.mdpi.com/2313-7673/8/2/170/htm
- https://www.mdpi.com/2076-0825/12/3/129
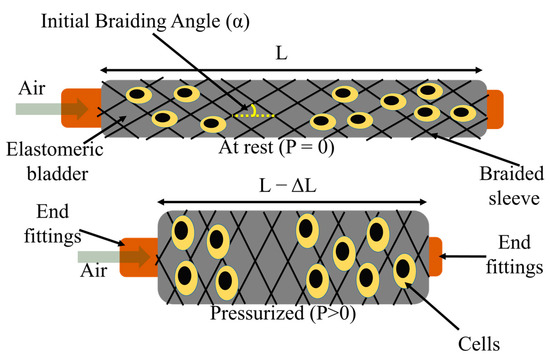
複雑な3次元動的培養システムとして使用するための空気圧駆動の繊維状ロボット足場の開発 Development of a Pneumatic-Driven Fiber-Shaped Robot Scaffold for Use as a Complex 3D Dynamic Culture System
Muh Amdadul Hoque,Nasif Mahmood,Kiran M. Ali,Eelya Sefa,Yihan Huan,Emily Peterse,Shane Harringto,Xiaomeng Fang and Jessica M. Gluck
Biomimetics Published: 21 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8020170
Abstract
Cells can sense and respond to different kinds of continuous mechanical strain in the human body. Mechanical stimulation needs to be included within the in vitro culture system to better mimic the existing complexity of in vivo biological systems. Existing commercial dynamic culture systems are generally two-dimensional (2D) which fail to mimic the three-dimensional (3D) native microenvironment. In this study, a pneumatically driven fiber robot has been developed as a platform for 3D dynamic cell culture. The fiber robot can generate tunable contractions upon stimulation. The surface of the fiber robot is formed by a braiding structure, which provides promising surface contact and adequate space for cell culture. An in-house dynamic stimulation using the fiber robot was set up to maintain NIH3T3 cells in a controlled environment. The biocompatibility of the developed dynamic culture systems was analyzed using LIVE/DEAD™ and alamarBlue™ assays. The results showed that the dynamic culture system was able to support cell proliferation with minimal cytotoxicity similar to static cultures. However, we observed a decrease in cell viability in the case of a high strain rate in dynamic cultures. Differences in cell arrangement and proliferation were observed between braided sleeves made of different materials (nylon and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene). In summary, a simple and cost-effective 3D dynamic culture system has been proposed, which can be easily implemented to study complex biological phenomena in vitro.
繊維状空気圧アクチュエータの性能に及ぼす材料特性の影響 Effect of Material Properties on Fiber-Shaped Pneumatic Actuators Performance
Muh Amdadul Hoque,Emily Petersen and Xiaomeng Fang
Actuators Published: 18 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/act12030129
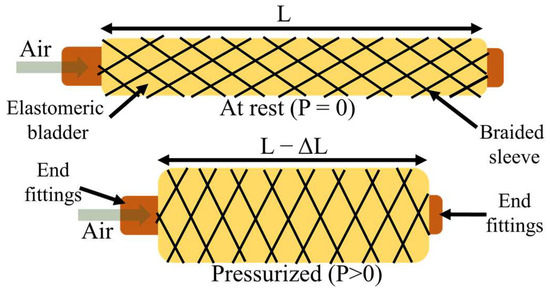
Abstract
Thin fiber-shaped pneumatic artificial muscle (PAM) can generate contractile motions upon stimulation, and it is well known for its good compliance, high weight-to-power ratio, resemblance to animal muscle movements, and, most importantly, the capability to be integrated into fabrics and other textile forms for wearable devices. This fiber-shaped device, based on McKibben technology, consists of an elastomeric bladder that is wrapped around by a braided sleeve, which transfers radial expansion into longitudinal contraction due to the change in the sleeve’s braiding angle while being inflated. This paper investigates the effect of material properties on fiber-shaped PAM’s behavior, including the braiding yarn and bladder’s dimensional and mechanical properties. A range of samples with combinations of yarn and bladder parameters were developed and characterized. A robust fabrication process verified through several calibration and control experiments of PAM was applied, which ensured a more accurate characterization of the actuators. The results demonstrate that material properties, such as yarn stiffness, yarn diameter, bladder diameter, and bladder hardness, have significant effects on PAMs’ deformation strains and forces generated. The findings can serve as fundamental guidelines for the future design and development of fiber-shaped pneumatic actuators.



