2023-02-09 ジョージア工科大学
◆今回、ジョージア工科大学の研究者は、マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)の研究者と共同で、2次元材料に基づく新しいプロセスを開発し、より小さく薄いピクセルを持つLEDディスプレイを作製することに成功しました。2次元材料に基づく層転写技術によって実現されたこの技術革新は、より鮮明でリアルなLEDディスプレイの未来を約束するものです。
◆研究チームは、2月に『Nature』誌に論文を発表しています。共著者には、韓国の世宗大学、さらに米国と韓国の研究機関の研究者も含まれています。
◆ジョージア工科大学欧州校のAbdallah Ougazzaden教授とSuresh Sundaram研究員は、MITの研究者と共同で、従来のLED製造プロセスを文字通り覆すことに成功しました。赤・緑・青(RGB)LEDを横に並べる従来のプロセスでは画素密度に限界がありましたが、研究チームは独立した極薄のRGB LED膜を垂直に積み重ね、1インチあたり5,100画素という配列密度を達成しました。これはこれまでに報告された中で最小の画素サイズ(4ミクロン)と史上最小の積層高さで、しかも商業用の全色を提供することが可能です。この超小型垂直スタックは、ジョージア工科大学・欧州研究所で開発された2次元窒化ホウ素上のファンデルワールスエピタキシー技術とMITで開発されたグラフェン上のリモートエピタキシー技術によって実現されたものである。
◆これらの高度な技術は、ウェーハスケールでのLED製造の主要ツールである有機金属化学気相成長法(MOCVD)リアクターで開発されたものです。2DLT技術は、高いスループット収率で産業規模に再現することができます。この技術は、仮想現実や拡張現実の分野を次のレベルに引き上げ、没入感のあるリアルな次世代マイクロLEDディスプレイを実現する可能性を持っています。
<関連情報>
- https://research.gatech.edu/researchers-pioneer-process-stack-micro-leds
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05612-1
2次元材料を用いた層間転写による縦型フルカラーマイクロLED Vertical full-colour micro-LEDs via 2D materials-based layer transfer
Jiho Shin,Hyunseok Kim,Suresh Sundaram,Junseok Jeong,Bo-In Park,Celesta S. Chang,Joonghoon Choi,Taemin Kim,Mayuran Saravanapavanantham,Kuangye Lu,Sungkyu Kim,Jun Min Suh,Ki Seok Kim,Min-Kyu Song,Yunpeng Liu,Kuan Qiao,Jae Hwan Kim,Yeongin Kim,Ji-Hoon Kang,Jekyung Kim,Doeon Lee,Jaeyong Lee,Justin S. Kim,Han Eol Lee,Hanwool Yeon,Hyun S. Kum,Sang-Hoon Bae,Vladimir Bulovic,Ki Jun Yu,Kyusang Lee,Kwanghun Chung,Young Joon Hong,Abdallah Ougazzaden
Nature Published:01 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05612-1
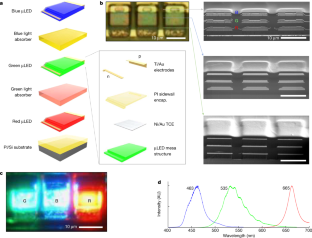
Abstract
Micro-LEDs (µLEDs) have been explored for augmented and virtual reality display applications that require extremely high pixels per inch and luminance1,2. However, conventional manufacturing processes based on the lateral assembly of red, green and blue (RGB) µLEDs have limitations in enhancing pixel density3,4,5,6. Recent demonstrations of vertical µLED displays have attempted to address this issue by stacking freestanding RGB LED membranes and fabricating top-down7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14, but minimization of the lateral dimensions of stacked µLEDs has been difficult. Here we report full-colour, vertically stacked µLEDs that achieve, to our knowledge, the highest array density (5,100 pixels per inch) and the smallest size (4 µm) reported to date. This is enabled by a two-dimensional materials-based layer transfer technique15,16,17,18 that allows the growth of RGB LEDs of near-submicron thickness on two-dimensional material-coated substrates via remote or van der Waals epitaxy, mechanical release and stacking of LEDs, followed by top-down fabrication. The smallest-ever stack height of around 9 µm is the key enabler for record high µLED array density. We also demonstrate vertical integration of blue µLEDs with silicon membrane transistors for active matrix operation. These results establish routes to creating full-colour µLED displays for augmented and virtual reality, while also offering a generalizable platform for broader classes of three-dimensional integrated devices.