2022-08-24 オーストラリア研究評議会研究センター(ARC)
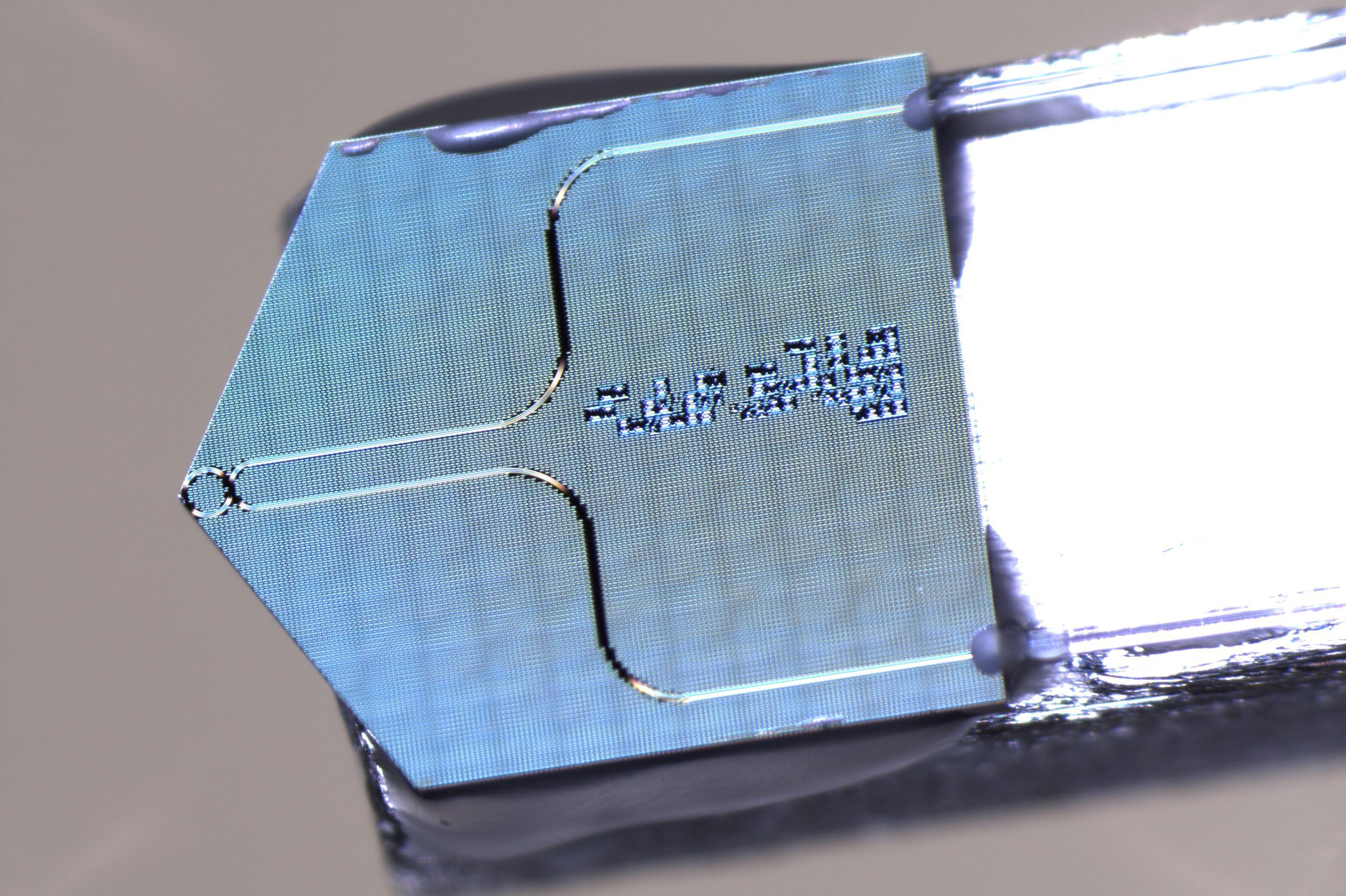
顕微鏡と特殊なレーザーを組み合わせた装置は、太陽電池内の欠陥の写真とマップを作成し、時間や使用によって電力や効率が低下している箇所を科学者に知らせる。また、その原因を示すデータも得られる。
マイクロ分光法の一例であるこの革新的な技術は、Jamie の個人的なプロジェクトとして始まり、もともとは鉱物を分析することを目的としていました。
レーザービームを使用して、スポットに焦点を当て、デバイス全体をスキャンして、太陽電池の品質を測定する。この新しい方法では、太陽電池全体、または完全な太陽電池の画像解析を行い、その性能、時間経過や老化による変化、太陽電池としての品質を見ることができる。
<関連情報>
- https://excitonscience.com/news/spare-room-outer-space-diy-project-could-transform-solar-power
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/smtd.202200493
次世代太陽電池のための強度変調光電流マイクロスペクトロスコピー Intensity Modulated Photocurrent Microspectrosopy for Next Generation Photovoltaics
Jamie S. Laird,Sandheep Ravishankar,Kevin J. Rietwyk,Wenxin Mao,Udo Bach,Trevor A. Smith
Small Methods Published: 16 August 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202200493

Abstract
In this report, a large-area laser beam induced current microscope that has been adapted to perform intensity modulated photocurrent spectroscopy (IMPS) in an imaging mode is described. Microscopy-based IMPS method provides a spatial resolution of the frequency domain response of the solar cell, allowing correlation of the optoelectronic response with a particular interface, bulk material, specific transport layer, or transport parameter. The system is applied to study degradation effects in back-contact perovskite cells where it is found to readily differentiate areas based on their markedly different frequency response. Using the diffusion-recombination model, the IMPS response is modeled for a sandwich structure and extended for the special case of lateral diffusion in a back-contact cell. In the low-frequency limit, the model is used to calculate spatial maps of the carrier ambipolar diffusion length. The observed frequency response of IMPS images is then discussed.