2026-02-10 東京科学大学
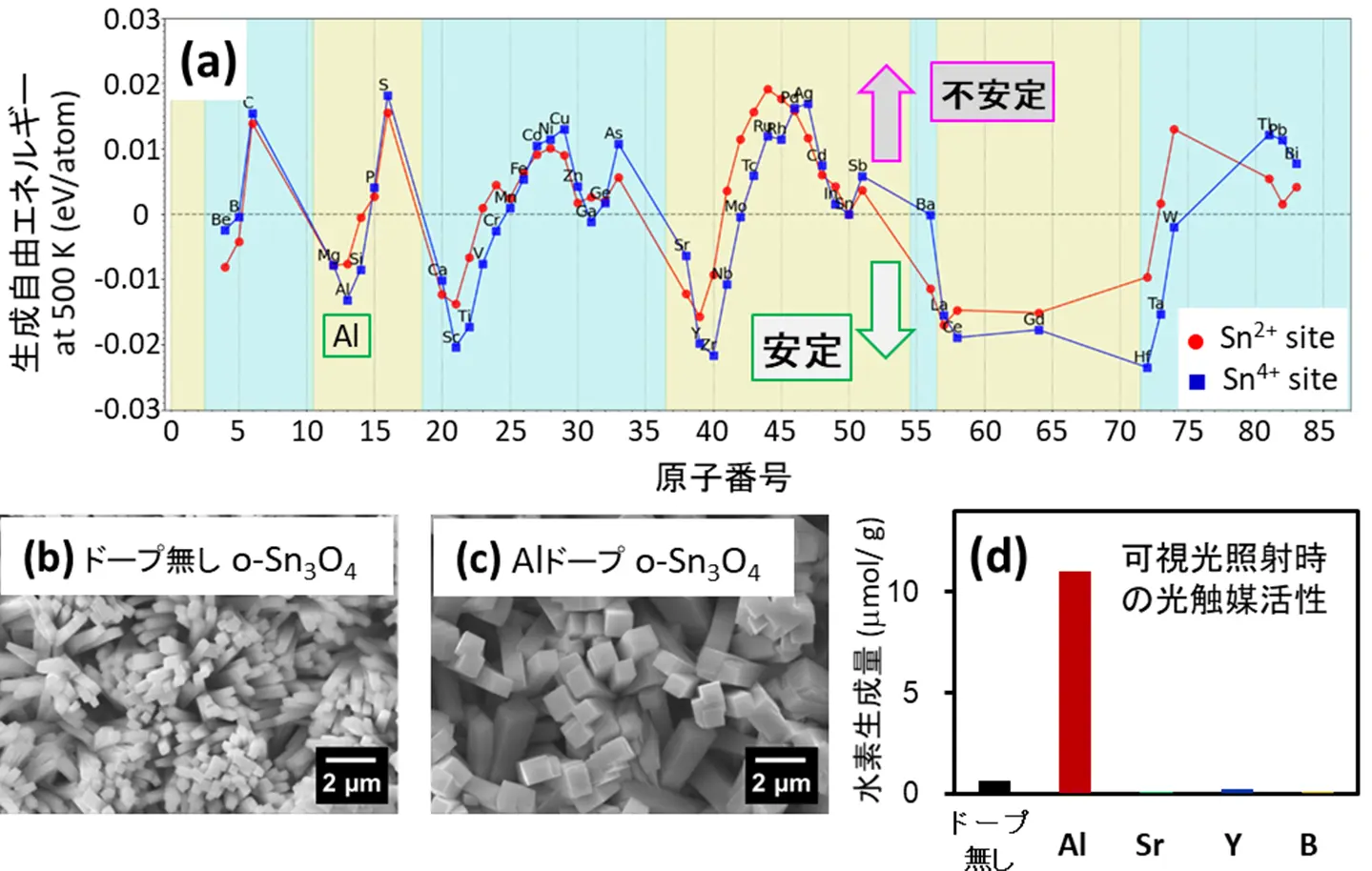
図1. (a)機械学習原子間ポテンシャル[用語5](MLIP)による各種イオンをドープしたo‑Sn3O4の生成自由エネルギー[用語6]の計算結果(生成自由エネルギーはドープしないo-Sn3O4の値を基準(ゼロ)とした)。
(b)、(c)はドープしていないo-Sn3O4とアルミニウムイオンをドープしたo-Sn3O4の走査型電子顕微鏡像。
(d)可視光照射下における水素生成量。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/jdmhtu6yr3mh
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=3175&prevId=&key=3bed826821d7e700485bf5ae2ae5e7ce.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c15962
可視光活性光触媒のための金属イオンドープ斜方晶系Sn 3O4の計算および実験による実現 Computational and Experimental Realization of Metal-Ion-Doped Orthorhombic Sn3O4 for Visible-Light-Active Photocatalysis
Sho Uchida,Yuta Sekine,Yohei Cho,Akira Yamaguchi,Toyokazu Tanabe,Kenji Yamaguchi,and Masahiro Miyauchi
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: February 3, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c15962
Abstract
The orthorhombic tri-tin tetraoxide (Sn3O4) is a newly discovered polymorph and has attracted great attention due to its visible-light absorption capability. To improve performance and broaden the material space based on orthorhombic Sn3O4, impurity doping represents a promising approach. In this study, we predict stable cation-doped orthorhombic Sn3O4 crystals using machine learning interatomic potential (MLIP) calculations. Several candidate cations such as boron (B), aluminum (Al), strontium (Sr), and yttrium (Y) have been predicted as stable dopants in orthorhombic Sn3O4 with low Gibbs energies of formation. Based on this prediction, we synthesized cation-doped Sn3O4 powder samples using a hydrothermal method. We confirmed that the cations predicted to be stable by the MLIP could be synthesized into the orthorhombic powder phase. Among the samples, the Al-doped Sn3O4 powder exhibited superior photocatalytic hydrogen production activity under visible light. Furthermore, we fabricated thin films of Al-doped Sn3O4 and optimized the doping amount of Al to achieve high photocatalytic activity. The 5% Al-doped Sn3O4 exhibited the highest activity owing to its high crystallinity and optimal morphology for better separation of photogenerated carriers. The Al-doped orthorhombic Sn3O4 is promising for application as a visible light-active photocatalyst.