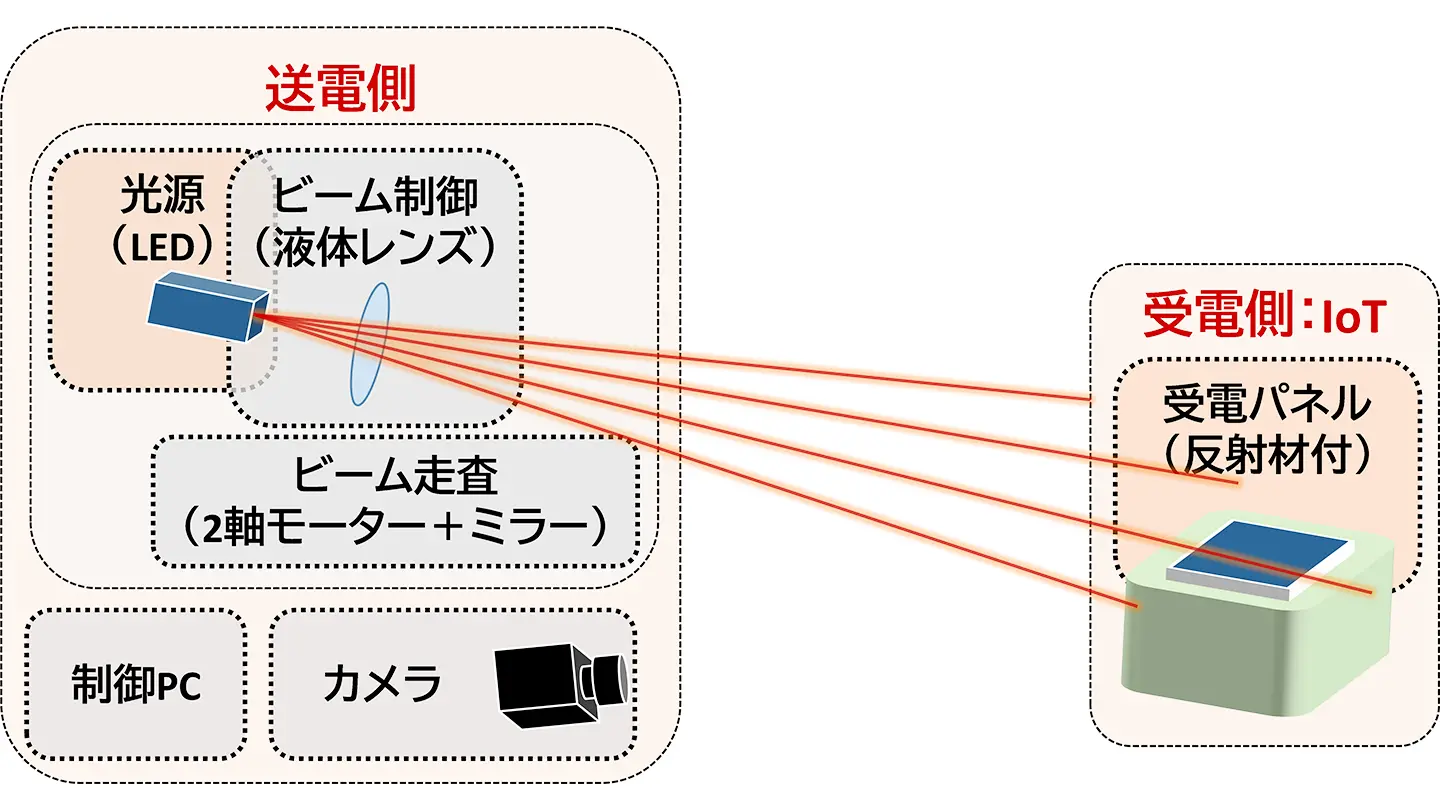
2025-10-28 中国科学院(CAS)
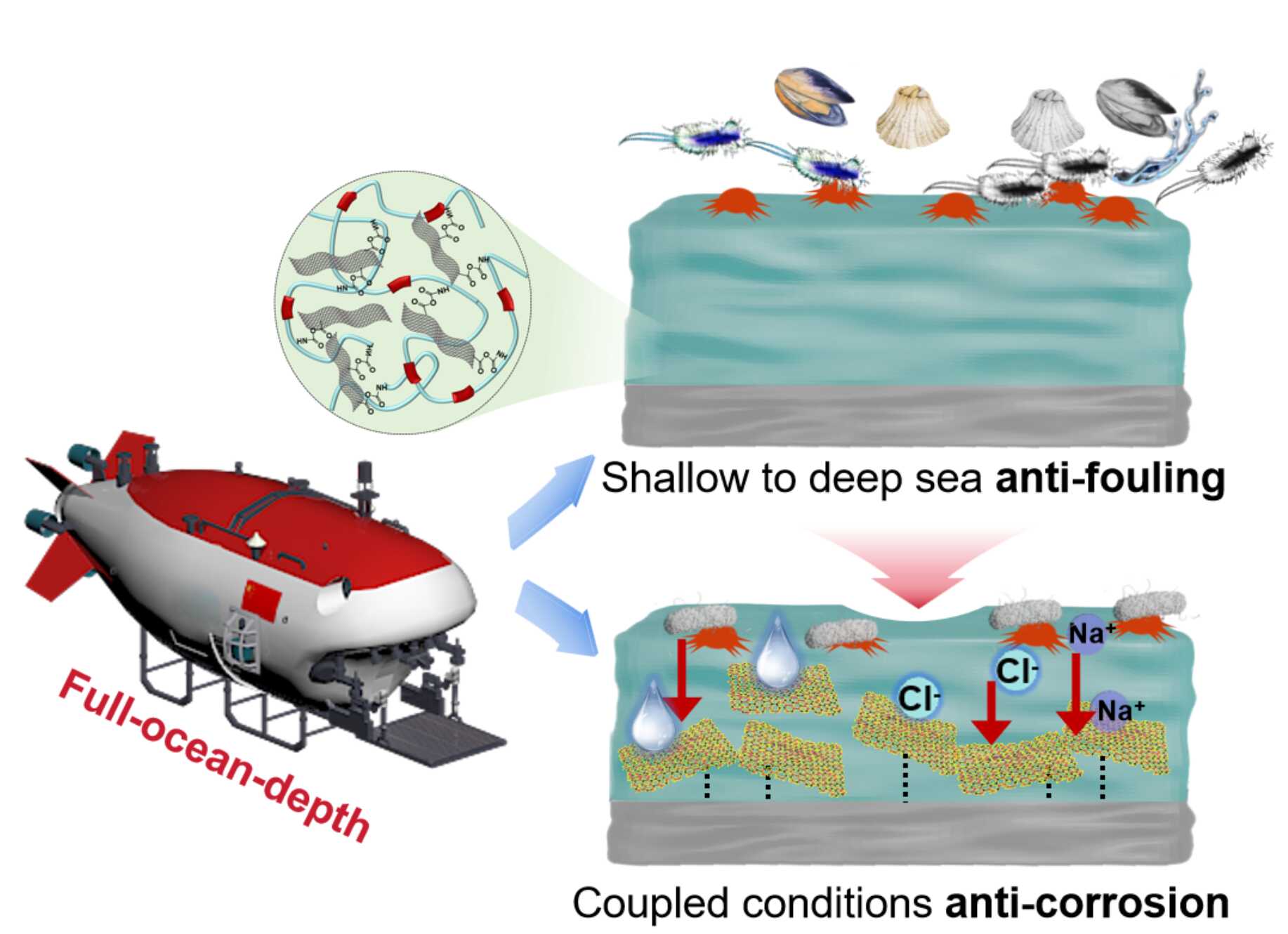
The full-ocean-depth-oriented coating for integrated antifouling and anticorrosion. (Image by NIMTE)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/tech/202510/t20251029_1095067.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.5c09595
海洋深層指向性ポリオキシムウレタンコーティング:防汚・防食一体型コーティングの構造と保護機構 Full-Ocean-Depth-Oriented Poly(oxime-urethane) Coating: Construction and Protective Mechanism for Integrated Antifouling and Anticorrosion
Peng Zhang,Shu Tian,Ruiqi Li,Guangming Lu,Qunji Xue,Liping Wang
ACS Nano Published: September 15, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5c09595
Abstract
Full-ocean-depth (FOD) environment, characterized by extreme pressure, salinity, and biological complexity, presents severe challenges for surface antifouling and anticorrosion. High-performance coatings capable of withstanding such coupled extreme conditions are urgently needed. Herein, an integrated antifouling/anticorrosion poly(oxime-urethane) (PUDF) coating with a tunable microphase-separated structure was developed by incorporating the intrinsically antifouling unit (2,5-diformylfuran dioxime, DFFD) and the reactive high-barrier nanosheets (carboxyl-functionalized graphene oxide GO-COOH). The coating showed excellent biointerface resistance, suppressing protein and bacterial biofilm adhesion by 98 and 99%, respectively, and achieving 100% bactericidal efficacy against marine bacteria. After 2 months of immersion at both shallow-sea (2 m, East China Sea) and deep-sea (7730 m, Philippine Sea) sites, no macrofouling organisms or deep-sea microbial adhesion were observed. Cross-linking GO-COOH within the PUDF matrix enhanced microphase separation and mechanical robustness, enabling exceptional resistance to coupled corrosion. Under a combined condition of 15 MPa, 3.5 wt % NaCl, and 106 cells mL–1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the coating exhibited impedance two orders of magnitude higher than pristine PUDF. Microbial community analysis and density functional theory (DFT) simulations further elucidated the disruption of purine biosynthesis/nucleotide metabolism antifouling and low-adsorption/high-barrier anticorrosion synergistic protection mechanisms. This study offers a theoretical and practical basis for designing integrated protection materials for FOD applications.