2025-07-13 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/infotech/202507/t20250714_1047354.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41378-025-00937-z
弱結合共振器を用いた新しい高性能広帯域真空センサー A novel high-performance wide-range vacuum sensor based on a weak-coupling resonator
Jiaxin Qin,Wenliang Xia,Junbo Wang,Deyong Chen,Yulan Lu,Xiaoye Huo,Bo Xie & Jian Chen
Microsystems & Nanoengineering Published:21 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-025-00937-z
Abstract
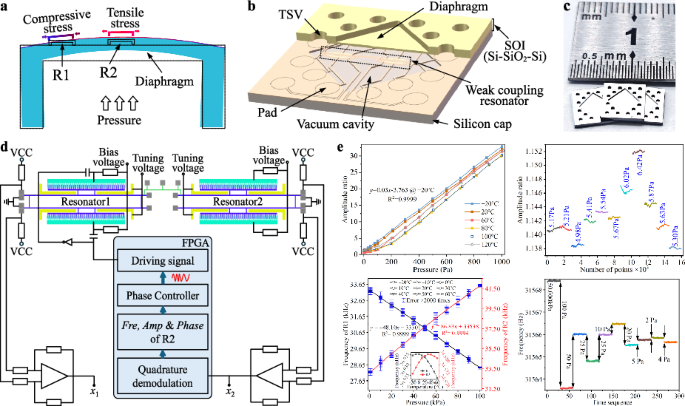
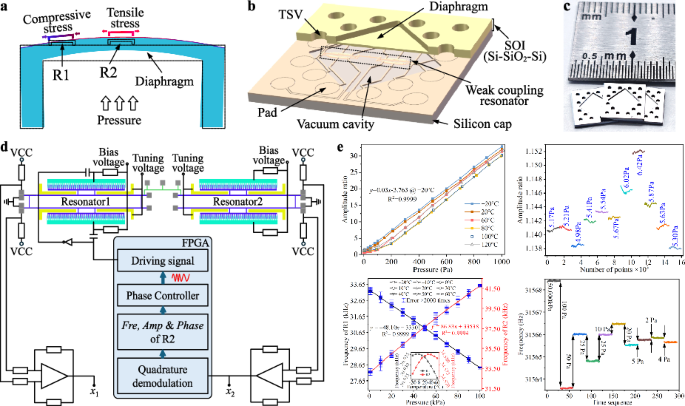
Wide-range vacuum sensors (0.1–105 Pa) are crucial for a variety of applications, particularly in semiconductor equipment. However, existing sensors often face a trade-off between measurement range and accuracy, with some offering a wide range at the expense of low accuracy, and others providing high accuracy within a limited range. This restricts their applicability in advanced technologies. The primary challenge lies in the sensitivity constraints at medium vacuum, the accuracy limitations at low vacuum, and the dependence of gas types. In this study, a new paradigm of high-performance wide-range MEMS diaphragm-based vacuum sensor is proposed, which is inherently small volume and independent of gas types. The sensor measures the vacuum pressure based on a two degree of freedom weak-coupling resonator, which operates in two distinct modes. In the range from 0.3 Pa to 103 Pa, it works in mode-localized mode, where amplitude ratio serves as the output to enhance sensitivity and resolution. For pressure ranging from 103 Pa to 105 Pa, it works in traditional resonance mode, with frequency serving as the output to achieve high accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed sensor outperforms conventional vacuum sensors.