2025-05-31 東京大学
東京大学とAGCは、次世代半導体用のガラス基板(EN-A1)に対し、深紫外レーザーを用いて直径10マイクロメートル以下、アスペクト比約20の微細穴あけ加工に成功しました。従来のエッチング法では困難だった高密度・高アスペクト比の穴あけを、クラックなしで実現。化学処理不要で環境負荷も低減します。成果は生成AIや6G通信などで期待されるチップレット技術を支えるガラス基板の実用化に貢献し、日本の半導体後工程分野での競争力強化が期待されます。
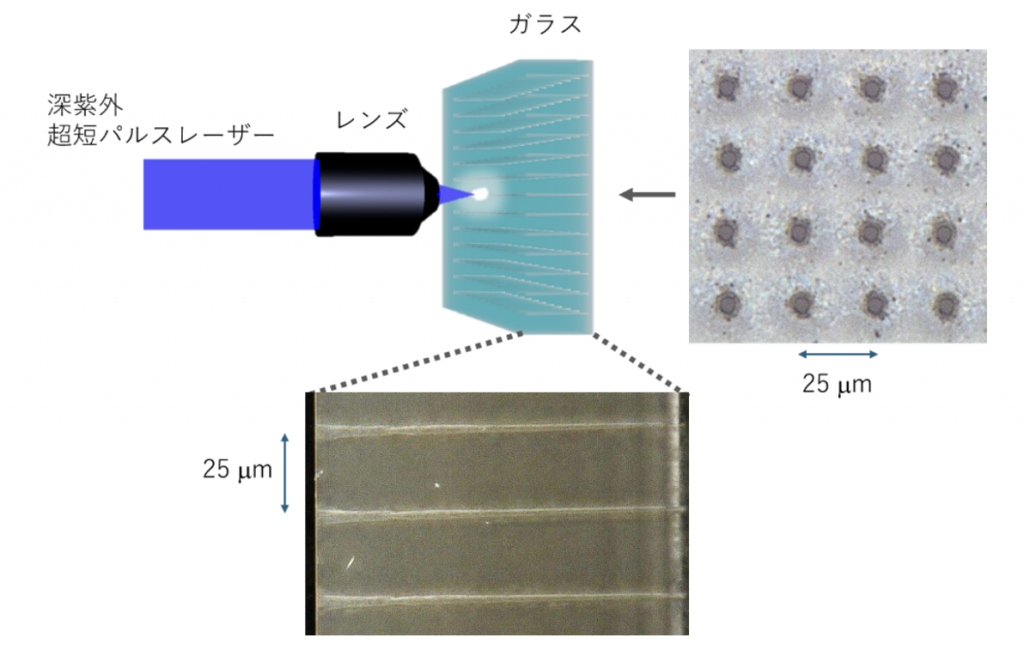
半導体基板ガラスへのレーザー微細穴あけ
次世代半導体の基板に用いられると期待されているEN-A1ガラスに対して、25マイクロメートル間隔で直径10マイクロメートル以下の穴あけ加工を深紫外レーザーで実現しました
<関連情報>
- https://www.issp.u-tokyo.ac.jp/maincontents/news2.html?pid=27304
- https://www.issp.u-tokyo.ac.jp/news/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/press_0529_press_-DUV-ENA1.pdf
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11038097
ドライレーザーマイクロドリル加工による厚さ100μmのEN-A1への高アスペクト比、直径6μmの貫通ガラスビア加工 High-aspect-ratio, 6-μm-diameter through-glass-via fabrication into 100-μm-thick EN-A1 by dry laser micro-drilling process
Toshio Otsu, Tsubasa Endo, Akihiro Shibata, Yoichiro Sato, Hiroharu Tamaru and Yohei Kobayashi
2025 IEEE 75th Electronic Components and Technology Conference Date Added to IEEE Xplore: 26 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1109/ECTC51687.2025.00179
Abstract:
In recent years, glass has attention as a core material for substrates and interposers due to its excellent highfrequency characteristics and coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) similar to silicon. In such applications, it is necessary to create a large number of fine through-holes in the glass. Currently, these vias are drilled using ultrafast laser induced selective etching. However, this process involves the use of hydrofluoric acid (HF), a hazardous substance, which poses a significant issue. Consequently, a direct laser processing technique is highly anticipated. In this study, we report on the direct laser drilling of glass without the use of etching. Using an ultrashort-pulse laser with a wavelength of 257 nm, we successfully drilled fine holes in 100μ m-thick ENA1 glass. Laser processing was performed with a pulse energy of 4μ J and 200 shots, achieving hole formation with a pitch of 25μ m and a hole diameter of 6μ m. The aspect ratio of the holes was 16.7, and the time required to drill a single hole was 4 ms. Furthermore, to investigate which laser parameters are crucial for creating high-aspect-ratio holes in thicker ENA1 glass, we collected data on the relationship between pulse energy, number of pulse, and hole geometry. The results revealed that hole depth is limited by pulse energy. The aspect ratio does not change largely since higher pulse energy makes larger hole diameter in high pulse energy region.