2024-04-29 イリノイ大学アーバナ・シャンペーン校
<関連情報>
- https://asc.illinois.edu/uncategorized/asc-study-successfully-uses-ground-far-red-sif-data-to-measure-canopy-level-photosynthesis/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-024-03004-w
米国中西部農業生態系における地上遠赤外太陽光誘発クロロフィル蛍光と植生指標 Ground far-red sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence and vegetation indices in the US Midwestern agroecosystems
Genghong Wu,Kaiyu Guan,Hyungsuk Kimm,Guofang Miao,Xi Yang & Chongya Jiang
Scientific Data Published:22 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03004-w
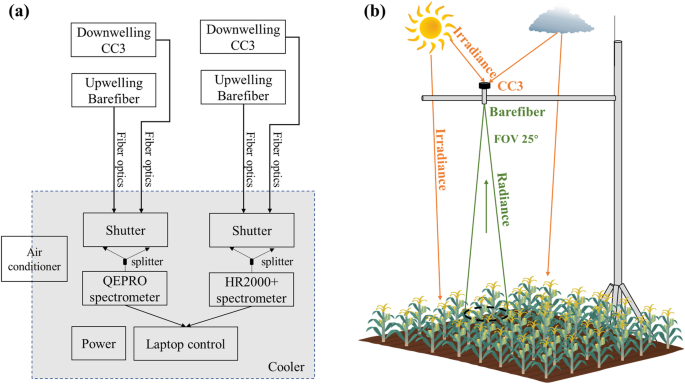
Abstract
Sun-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) provides an opportunity to study terrestrial ecosystem photosynthesis dynamics. However, the current coarse spatiotemporal satellite SIF products are challenging for mechanistic interpretations of SIF signals. Long-term ground SIF and vegetation indices (VIs) are important for satellite SIF validation and mechanistic understanding of the relationship between SIF and photosynthesis when combined with leaf- and canopy-level auxiliary measurements. In this study, we present and analyze a total of 15 site-years of ground far-red SIF (SIF at 760 nm, SIF760) and VIs datasets from soybean, corn, and miscanthus grown in the U.S. Corn Belt from 2016 to 2021. We introduce a comprehensive data processing protocol, including different retrieval methods, calibration coefficient adjustment, and nadir SIF footprint upscaling to match the eddy covariance footprint. This long-term ground far-red SIF and VIs dataset provides important and first-hand data for far-red SIF interpretation and understanding the mechanistic relationship between far-red SIF and canopy photosynthesis across various crop species and environmental conditions.