2023-08-24 ロスアラモス国立研究所(LANL)
◆この成果は、量子情報と通信の分野で重要な進歩であり、量子暗号学や通信に応用が期待されます。磁場や複雑な光学構造などの高コストな手法を必要とせず、低コストで信頼性の高い光源を実現しました。これにより、量子情報技術の発展に寄与する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://discover.lanl.gov/news/0824-quantum-light-emissions/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-023-01645-7
歪み制御されたWSe2/NiPS3ヘテロ構造における近接誘起キラル量子光発生 Proximity-induced chiral quantum light generation in strain-engineered WSe2/NiPS3 heterostructures
Xiangzhi Li,Andrew C. Jones,Junho Choi,Huan Zhao,Vigneshwaran Chandrasekaran,Michael T. Pettes,Andrei Piryatinski,Märta A. Tschudin,Patrick Reiser,David A. Broadway,Patrick Maletinsky,Nikolai Sinitsyn,Scott A. Crooker & Han Htoon
Nature MaterialsPublished:17 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01645-7
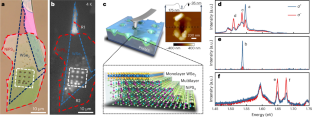
Abstract
Quantum light emitters capable of generating single photons with circular polarization and non-classical statistics could enable non-reciprocal single-photon devices and deterministic spin–photon interfaces for quantum networks. To date, the emission of such chiral quantum light relies on the application of intense external magnetic fields, electrical/optical injection of spin-polarized carriers/excitons or coupling with complex photonic metastructures. Here we report the creation of free-space chiral quantum light emitters via the nanoindentation of monolayer WSe2/NiPS3 heterostructures at zero external magnetic field. These quantum light emitters emit with a high degree of circular polarization (0.89) and single-photon purity (95%), independent of pump laser polarization. Scanning diamond nitrogen-vacancy microscopy and temperature-dependent magneto-photoluminescence studies reveal that the chiral quantum light emission arises from magnetic proximity interactions between localized excitons in the WSe2 monolayer and the out-of-plane magnetization of defects in the antiferromagnetic order of NiPS3, both of which are co-localized by strain fields associated with the nanoscale indentations.