2023-03-28 カリフォルニア大学バークレー校(UCB)
アメリカ・バークレー大学の天文学・物理学のRaffaella Margutti准教授は、モデルが複雑でないため、このような結果になったと説明した。彼女は、ガンマ線バーストが検出された後、世界中の望遠鏡を動員してデータを収集し、この現象に関する多数の観測データを集めることに成功した。
この結果は、ハワイで開催されたアメリカ天文学会の高エネルギー天体物理学分科会で発表された。
<関連情報>
- https://news.berkeley.edu/2023/03/28/bright-gamma-ray-burst-confounds-models-of-black-hole-birth/
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/2041-8213/acbfad
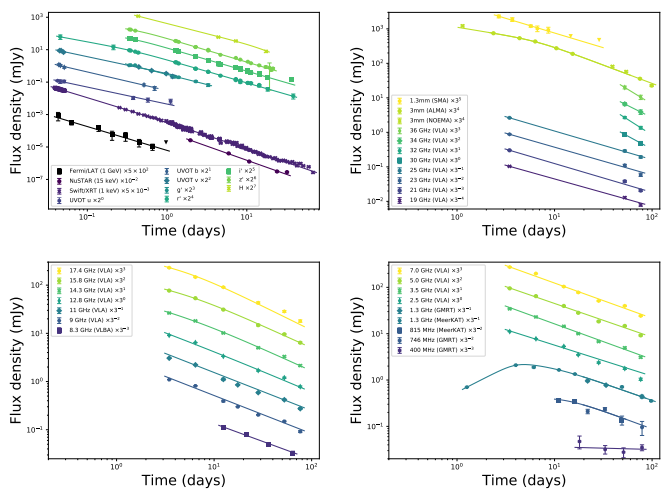
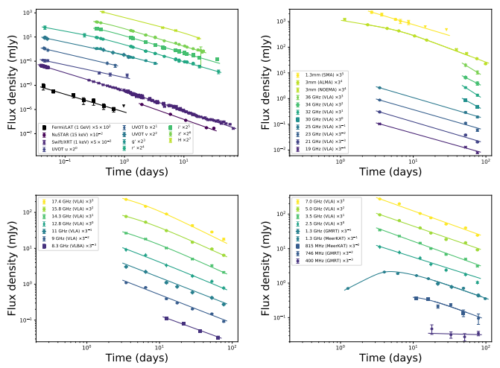
GRB221009Aの電波からGeVまでの残光 The Radio to GeV Afterglow of GRB 221009A
Tanmoy Laskar, Kate D. Alexander, Raffaella Margutti, Tarraneh Eftekhari, Ryan Chornock, Edo Berger,Yvette Cendes, Anne Duerr, Daniel A. Perley, Maria Edvige Ravasio,Ryo Yamazaki, Eliot H. Ayache,Thomas Barclay, Rodolfo Barniol Duran,Shivani Bhandari, Daniel Brethauer, Collin T. Christy, Deanne L. Coppejans, Paul Duffell, Wen-fai Fong, Andreja Gomboc, Cristiano Guidorzi, Jamie A. Kennea, Shiho Kobayashi, Andrew Levan, Andrei P. Lobanov, Brian D. Metzger, Eduardo Ros, Genevieve Schroeder and P. K. G. Williams
The Astrophysical Journal Letters Published:2023 March 28
DOI:10.3847/2041-8213/acbfad
Abstract
GRB 221009A (z = 0.151) is one of the closest known long γ-ray bursts (GRBs). Its extreme brightness across all electromagnetic wavelengths provides an unprecedented opportunity to study a member of this still-mysterious class of transients in exquisite detail. We present multi-wavelength observations of this extraordinary event, spanning 15 orders of magnitude in photon energy from radio to γ-rays. We find that the data can be partially explained by a forward shock (FS) from a highlycollimated relativistic jet interacting with a low-density wind-like medium. Under this model, the jet’s beaming-corrected kinetic energy (EK ∼ 4 × 1050 erg) is typical for the GRB population. The radio and mm data provide strong limiting constraints on the FS model, but require the presence of an additional emission component. From equipartition arguments, we find that the radio emission is likely produced by a small amount of mass (. 6 × 10−7M ) moving relativistically (Γ & 9) with a large kinetic energy (& 1049 erg). However, the temporal evolution of this component does not follow prescriptions for synchrotron radiation from a single power-law distribution of electrons (e.g. in a reverse shock or two-component jet), or a thermal electron population, perhaps suggesting that one of the standard assumptions of afterglow theory is violated. GRB 221009A will likely remain detectable with radio telescopes for years to come, providing a valuable opportunity to track the full lifecycle of a powerful relativistic jet.