2023-01-23 パシフィックノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)

・ PNNL が、CO2 を効率的に捕獲してメタノールに変換する、これまでで最も安価なシステムを開発。
・ 温暖化緩和の鍵は大気への CO2 排出抑制だが、商用の炭素捕獲技術の高いコストが技術普及の長年の障壁であるため、大規模な排出源による炭素捕獲技術導入のインセンティブの創出が重要。
・PNNL では、CO2 を利用して得られるメタノールがこのようなインセンティブを提供すると考える。
・ 新システムは、石炭、ガス、バイオマスによる火力発電所に加え、セメントキルンや鉄工所への設置も可能な設計。PNNL が特許を取得した CO2 吸着剤「CO2BOL」により、大気への排出前に CO2 を捕獲してメタノールに変換する。メタノールは、プラスチック、塗料、建築資材や自動車部品等の主要なプラットフォーム原料。
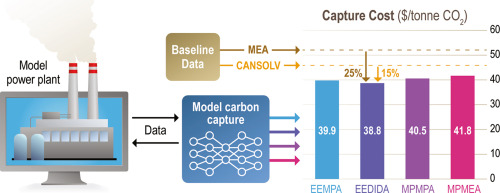
・ 1 トンあたり約 46 ドルの現行商用システムによる燃焼排ガスからの CO2 除去コストを 39 ドルに低減し、CO2 捕獲とメタノールへの変換を一括して行うモノリシックなフローシステムを実現。また、従来技術に使用される高純度 CO2 が不要で、「汚れた」CO2 を使用できる。
・ 新システムは、CO2 排出量を削減すると同時に他の炭素捕獲技術開発の促進と CO2 含有材料の市場の確立に貢献するもの。このような市場の存在は、直接空気回収(DAC)技術で捕獲した炭素の永続的な材料への再構築を進展させる可能性がある。
・ 気候変動に関する政府間パネル(IPCC)の第 6 次評価報告書(AR6)WG3 報告書では、「社会に必要な炭素(プラスチック、木材、航空機燃料、溶剤等)のネットゼロ排出実現において、機械・化学リサイクルの資源循環を通じた炭素と CO2 の利用のループを閉じることの重要性に言及している。
・ 本研究は、米国エネルギー省(DOE)の Carbon Negative Shot に即したもので、CO2 変換に再生可能水素を利用し、天然ガス使用の従来技術よりもカーボンフットプリントを低く抑える。ギ酸やメタン等、他の物質への変換も可能。ポリウレタン、ポリエステルへの変換も目指す。
・ 発電所内や近隣に CO2 リファイナリを設け、CO2 含有材料のオンサイト製造等を構想。新システムの最適化やスケールアップ等が課題で、商業利用は数年先となる。新システム技術のライセンス供与が可能。
・ 本研究は、米国エネルギー省(DOE) Technology Commercialization Fund、化石エネルギー・炭素管理局(FECM)およびサザンカリフォルニアガスが支援した。
URL: https://www.pnnl.gov/news-media/scientists-unveil-least-costly-carbon-capture-system-date
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
関連情報
Journal of Cleaner Production 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
Energy-effective and low-cost carbon capture from point-sources enabled by water-lean solvents
URL: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652622052702?via%3Dihub
関連情報
PNNL 開発の(特許取得済み)CO2 捕獲溶剤の詳細
CO2BOL Solvents for Cheaper Carbon Capture and Sequestration, Pre- and Post-Combustion
URL: https://www.pnnl.gov/available-technologies/co2bol-solvents-cheaper-carbon-capture-and-sequestration-pre-and-post
Abstract
Aqueous amines, as the most mature carbon capture technology, are subject to high energy and cost penalties due to the large water content in their formulations. Emerging technologies are in demand to enable a transition to a low-carbon global economy. However, rigorous process modeling and techno-economic analyses are limited for emerging carbon capture technologies. Here, four CO2-Binding Organic Liquids (CO2BOLs), all water-lean solvents were presented as promising options towards energy-effective and low-cost carbon capture from point sources. Rigorous solvent property and process models were developed in Aspen Plus for a coal-fired power plant with CO2BOL-based carbon capture unit. Techno-economic analyses were conducted in 2018 US pricing basis. The results suggest that water-lean formulations can minimize water condensation and vaporization, leading to a 36% energy saving compared with aqueous amines. Indeed, these CO2BOLs can capture up to 97–99% CO2 from coal fired plant. The estimated carbon capture cost is about $40/tonne CO2 at 90–97% carbon capture rate, about 12–23% less expensive than the conventional aqueous amine technology. The comparison between these CO2BOLs showed that in addition to vapor liquid equilibrium and kinetics (key properties for aqueous solvents), viscosity, volatility, and hydrophobicity, also have strong impacts on the performance of water-lean solvents. The methods presented in this work can be used to evaluate other emerging carbon capture technologies, while the results linking costs and performance of carbon capture solvents with their properties. Further, this work identifies research directions and targets for further reductions in total costs of capture from either cost or energy perspectives for these leading water-lean solvents.