ジェームズ・ウェッブ宇宙望遠鏡のターゲットを絞り込む研究 Study narrows James Webb Space Telescope targets
2023-03-22 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
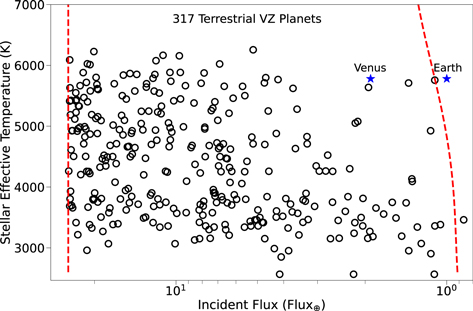
◆この論文を書いた科学者たちは、他の星に周回する300以上の既知の地球型惑星である系外惑星から始めました。彼らは、半径、質量、密度、軌道の形状、そしておそらく最も重要なことに、恒星からの距離に関して金星に似ていると思われる5つにリストを絞り込みました。
◆この論文は、The Astronomical Journalに掲載され、彼らが周回する恒星の明るさに関して最も金星に似た惑星をランク付けしました。これにより、大気の組成に関する情報をより詳細に取得できる可能性が高くなる。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2023/03/22/hunting-venus-20-scientists-sharpen-their-sights
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-3881/acbfaf
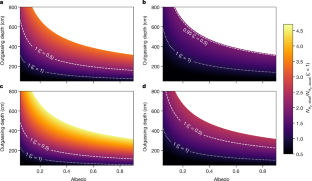
金星帯の地球型惑星の人口動態について The Demographics of Terrestrial Planets in the Venus Zone
Colby Ostberg, Stephen R. Kane, Zhexing Li, Edward W. Schwieterman, Michelle L. Hill, Kimberly Bott, Paul A. Dalba, Tara Fetherolf, James W. Head and Cayman T. Unterborn
The Astronomical Journal Published 2023 March 21
DOI:10.3847/1538-3881/acbfaf
Abstract
Understanding the physical characteristics of Venus, including its atmosphere, interior, and its evolutionary pathway with respect to Earth, remains a vital component for terrestrial planet evolution models and the emergence and/or decline of planetary habitability. A statistical strategy for evaluating the evolutionary pathways of terrestrial planets lies in the atmospheric characterization of exoplanets, where the sample size provides sufficient means for determining required runaway greenhouse conditions. Observations of potential exo-Venuses can help confirm hypotheses about Venus’s past, as well as the occurrence rate of Venus-like planets in other systems. Additionally, the data from future Venus missions, such as DAVINCI, EnVision, and VERITAS, will provide valuable information regarding Venus, and the study of exo-Venuses will be complimentary to these missions. To facilitate studies of exo-Venus candidates, we provide a catalog of all confirmed terrestrial planets in the Venus zone, including transiting and nontransiting cases, and quantify their potential for follow-up observations. We examine the demographics of the exo-Venus population with relation to stellar and planetary properties, such as the planetary radius gap. We highlight specific high-priority exo-Venus targets for follow-up observations, including TOI-2285 b, LTT 1445 A c, TOI-1266 c, LHS 1140 c, and L98–59 d. We also discuss follow-up observations that may yield further insight into the Venus/Earth divergence in atmospheric properties.