2022-11-16 カーネギーメロン大学
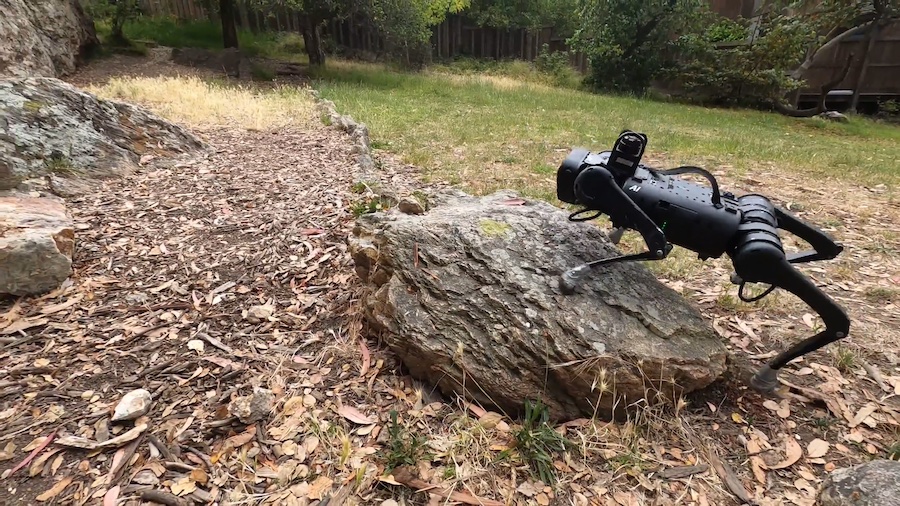

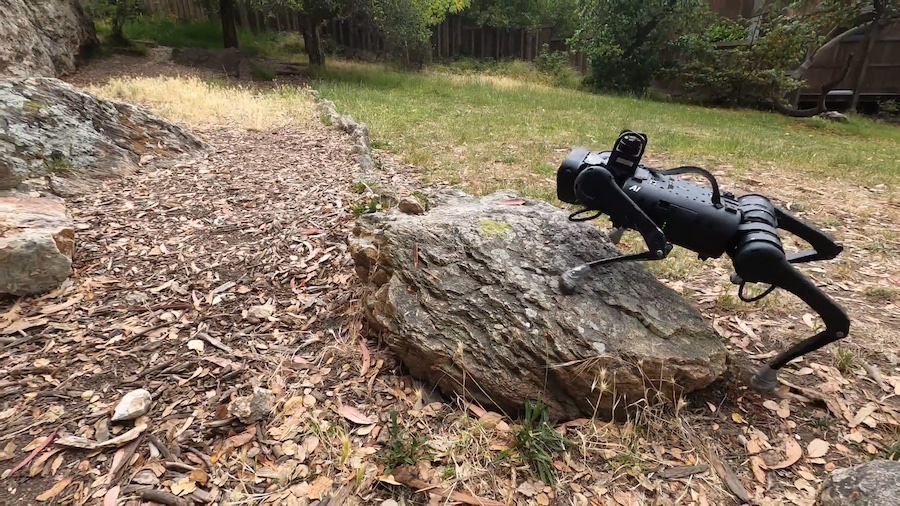
・ カーネギーメロン大学とカリフォルニア大学バークレー校(UCB)が、マッピングやプランニング無しで様々な環境下での小型四足歩行ロボットの動作を可能にするロボティックシステムを開発。
・ ロボット本体とほぼ同じ高さの階段の昇降、岩場や急傾斜、滑りやすい環境や、暗闇での動作等が可能となり、歩行ロボットの課題解決と家庭へのロボット導入に向けた大きな進展となる。
・ 一般的なロボットシステムによる周囲環境のマッピングと動作のプランニングの工程の進行は遅く、マッピング段階でのあいまいさや誤認で効果が弱まり、その後のプランニングや動作に影響を及ぼすことがある。高レベルの制御用システムには有効だが、複雑な地形での歩行・疾走等の低レベルスキルの動的要件には必ずしも適切ではない。
・ 新ロボティックシステムでは、このようなマッピングやプランニングを不要とし、ロボットに搭載した深度カメラとオンボードコンピューターを利用して複雑な地形での歩行・疾走のタスクを習得する。
・ カメラによる視覚情報と本体からのフィードバック情報をインプットし、オンボードコンピューターを通じてモーターへのコマンドをアウトプットする。実際の環境でも安定した動作が可能で、階段で転倒しても復帰し、未知の環境にも順応する。
・ 約 4,000 体のクローンロボットをシミュレーターで訓練することで、6 年間に相当する経験量をわずか一日で習得する。習得した運動技能はロボットにコピーできる。機械学習を利用した訓練のため、コストは標準的な四足ロボットの 1/25。
・ 過去の研究でカメラ無しのロボットで複雑な地形の歩行に成功している。人間や動物が視覚情報を利用して動作する能力に着想し、視覚情報の追加とその利用によりロボティックシステムを飛躍的に向上させた。
・ また、前脚で回避した障害物を後脚も同様に回避する、四足動物の脚の働きも採用した。フロントのカメラが捉えた障害物をシステムのオンボードメモリが後脚に記憶させて障害物を回避する。
・ さらに、背の高い障害物を踏み越える際の人間の腰回りの外転・内転運動をロボット設計に取り入れ、多くの商用歩行ロボットが苦手とする障害物の課題に対処した。
URL: https://www.scs.cmu.edu/news/2022/visual-locomotion
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
関連情報
2022 Conference on Robot Learning(CORL)発表論文(フルテキスト)
Legged Locomotion in Challenging Terrains using Egocentric Vision
URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.07638
Animals are capable of precise and agile locomotion using vision. Replicating this ability has been a long-standing goal in robotics. The traditional approach has been to decompose this problem into elevation mapping and foothold planning phases. The elevation mapping, however, is susceptible to failure and large noise artifacts, requires specialized hardware, and is biologically implausible. In this paper, we present the first end-to-end locomotion system capable of traversing stairs, curbs, stepping stones, and gaps. We show this result on a medium-sized quadruped robot using a single front-facing depth camera. The small size of the robot necessitates discovering specialized gait patterns not seen elsewhere. The egocentric camera requires the policy to remember past information to estimate the terrain under its hind feet. We train our policy in simulation. Training has two phases – first, we train a policy using reinforcement learning with a cheap-to-compute variant of depth image and then in phase 2 distill it into the final policy that uses depth using supervised learning. The resulting policy transfers to the real world and is able to run in real-time on the limited compute of the robot. It can traverse a large variety of terrain while being robust to perturbations like pushes, slippery surfaces, and rocky terrain. Videos are at this https URL