自動運転車やその他のアプリケーションの画像処理を高速化・簡略化するデバイスを開発 Device speeds up, simplifies image processing for autonomous vehicles and other applications
2022-08-25 ハーバード大学
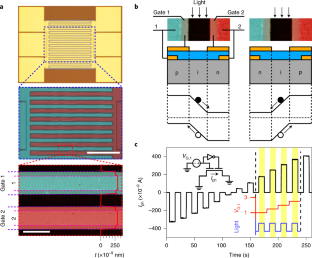
研究チームのシリコンフォトダイオードは静電ドープされており、入射光に対する個々のフォトダイオード(ピクセル)の感度を電圧で調整することができる。電圧可変フォトダイオードを複数個つなげたアレイは、多くの画像処理パイプラインで中心的な役割を果たす乗算や加算のアナログ版となり、画像を取り込むと同時に関連する視覚情報を抽出することができる。電圧可変フォトダイオードを複数個つなげたアレイは、多くの画像処理パイプラインで中心的な役割を果たす乗算や加算のアナログ版となり、画像を取り込むと同時に関連する視覚情報を抽出することができる。
シリコンフォトダイオードアレイは、さまざまな用途に合わせて、不要な細部やノイズを除去するためのさまざまな画像フィルターにプログラムすることができる。
<関連情報>
- https://www.seas.harvard.edu/news/2022/08/silicon-image-sensor-computes
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-022-00819-6
静電ドープシリコンを用いたインセンサ光電子コンピューティング In-sensor optoelectronic computing using electrostatically doped silicon
Houk Jang,Henry Hinton,Woo-Bin Jung,Min-Hyun Lee,Changhyun Kim,Min Park,Seoung-Ki Lee,Seongjun Park & Donhee Ham
Nature Electronics
Abstract
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) image sensors allow machines to interact with the visual world. In these sensors, image capture in front-end silicon photodiode arrays is separated from back-end image processing. To reduce the energy cost associated with transferring data between the sensing and computing units, in-sensor computing approaches are being developed where images are processed within the photodiode arrays. However, such methods require electrostatically doped photodiodes where photocurrents can be electrically modulated or programmed, and this is challenging in current CMOS image sensors that use chemically doped silicon photodiodes. Here we report in-sensor computing using electrostatically doped silicon photodiodes. We fabricate thousands of dual-gate silicon p–i–n photodiodes, which can be integrated into CMOS image sensors, at the wafer scale. With a 3 × 3 network of the electrostatically doped photodiodes, we demonstrate in-sensor image processing using seven different convolutional filters electrically programmed into the photodiode network.