2026-01-15 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
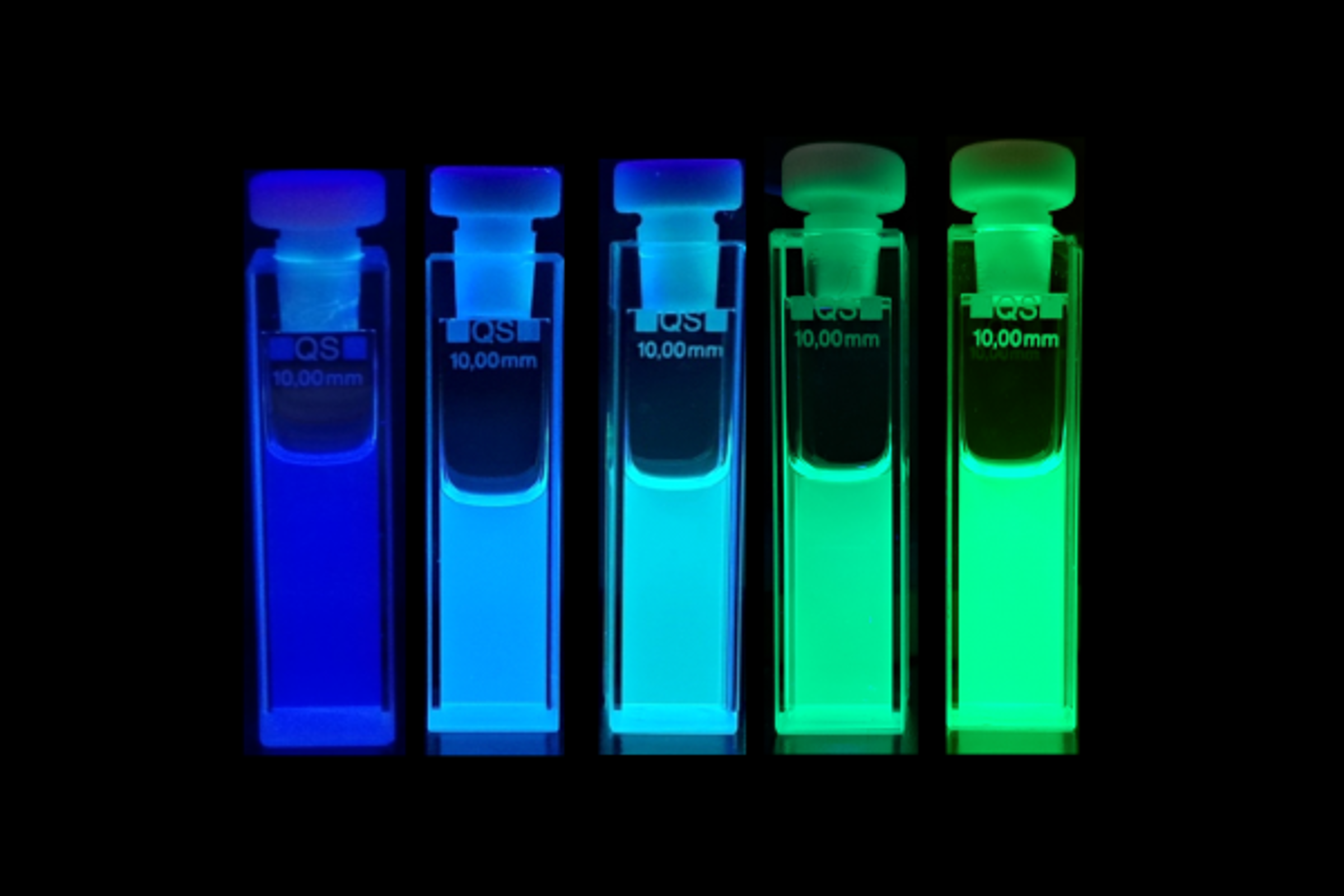

Perovskite nanocrystal solutions with different blue-green emission colors | © N. Henke / LMU
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/composing-nanomaterials-with-ai-and-chemistry-12dbb2aa.html
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202509472
シンセサイザー:ナノ結晶成長の精密制御のための化学を考慮した機械学習 Synthesizer: Chemistry-Aware Machine Learning for Precision Control of Nanocrystal Growth
Nina A. Henke, Leo Luber, Ioannis Kouroudis, Jonathan Paul, Alexander Schuhbeck, Lukas M. Rescher, Tizian Lorenzen, Veronika Mayer, Knut Müller-Caspary, Bert Nickel, Alessio Gagliardi, Alexander S. Urban
Advanced Materials Published: 05 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202509472
Abstract
Precise and reproducible control over nanocrystal synthesis is essential for tailoring optical properties, yet remains a long-standing challenge in halide perovskites. A broadly adoptable machine learning–guided framework, the Synthesizer, is introduced that combines Gaussian Process regression and Bayesian optimization with chemistry-aware molecular encodings and systematic feature engineering. Rather than new algorithms, the advance lies in translating interpretable machine learning tools into a practical, benchtop platform for nanocrystal optimization under ambient conditions. Using CsPbBr3 as a model system, nm-level precision in photoluminescence peak tuning (430 nm to 520 nm) is achieved, along with benchmark narrow linewidths down to 70 meV via lateral confinement control, and robust photoluminescence quantum yield optimization linked to surface trap density. Mapping the two-dimensional parameter space (Cs/PbBr2 and antisolvent/PbBr2 ratios) across multiple antisolvents enables predictive optimization and identifies the antisolvent/PbBr2 ratio as a previously underappreciated mechanistic parameter, offering a quantitative basis for antisolvent-accelerated nanocrystal growth. Transfer tests across distinct chemical spaces, including alcohols and cyclopentanone, confirm generalizability to unseen molecules, while application to CsPbI3 demonstrates extension to new material systems. These results establish an adoption-ready platform for data-efficient, uncertainty-aware synthesis design, providing reproducible pathways to accelerate materials discovery beyond halide perovskites.