2026-01-07 東京科学大学,科学技術振興機構
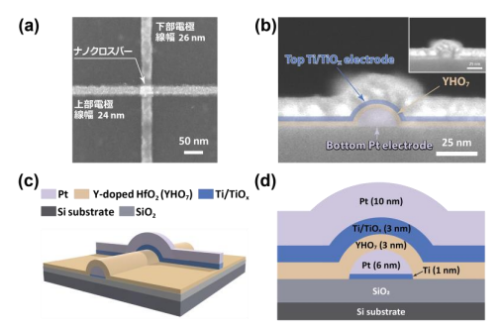
図 1 (a)25 nm スケールのナノクロスバー構造の Ti/TiOx/YHO7(3 nm)/Pt 強誘電トンネル接合(FTJ)の上面 SEM 画像。(b)ナノクロスバーTi/YHO7/Pt 構造の断面 SEM 画像。 Ti/TiOx層(青)、YHO7層(淡黄褐色)、Pt 層(紫)。右上挿入図に原画像を示す。(c)ナノクロスバーTi/TiOx/YHO7/Pt FTJ の 3D 模式図および(d)断面図。
<関連情報>
- https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20260107/index.html
- https://www.jst.go.jp/pr/announce/20260107/pdf/20260107.pdf
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2025/NR/D5NR04010H
25 nm TiOx/YドープHfO 2 /Ptナノクロスバー強誘電体トンネル接合 における高抵抗状態トンネリング High-Resistance-State Tunneling in 25 nm TiOx/Y-Doped HfO2/Pt Nanocrossbar Ferroelectric Tunnel Junctions
Zhongzheng Sun, Yoshiko Nakamura, Kazuki Okamoto, Seiichiro Izawa, Hiroshi Funakubo and Yutaka Majima
Nanoscale Published:02 Jan 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D5NR04010H
Abstract
We report nanocrossbar-type ferroelectric tunnel junctions (FTJs) with a Ti/TiOx/7% yttrium-doped HfO2 (YHO7)/Pt structure integrated on thermally oxidized Si substrates, which exhibit clear direct tunneling conduction even in the high-resistance state (HRS) and a tunneling electroresistance ratio exceeding 103. The nanocrossbar FTJs were fabricated using a double-exposure electron-beam lithography (EBL) process with lateral dimensions scaled down to 25 nm. The temperature dependence of the TER effect measurements at 9 and 300 K confirms that both low-and high-resistance states are dominated by the direct tunneling conduction. A maximum TER ratio of 2.2 × 103 was obtained in a 3 nm-thick YHO7 nanocrossbar FTJ with an effective area of 26 × 24 nm2. The FTJ area was reduced from 42,000 to 255 nm2, and the scaling behavior of the TER effect in 3 nm-thick YHO7 devices closely resemble that in 2 nm-thick devices. The OFF-state current decreased with a slope of 1.1 between 42,000 and 2,600 nm2, followed by a steeper reduction below 2,600 nm2, whereas the ON-state current decreased more gradually with a slope of 0.30. These contrasting area dependences are attributed to the suppression of leakage pathways along grain boundaries in the OFF state and uniformly aligned remanent polarization in a small number of grains in the ON state. The demonstrated nanocrossbar FTJs highlight a promising route toward high-density, energy-efficient, and CMOS-compatible integration of ferroelectric memory.