2025-12-23 千葉工業大学,基礎生物学研究所,兵庫県立大学
<関連情報>
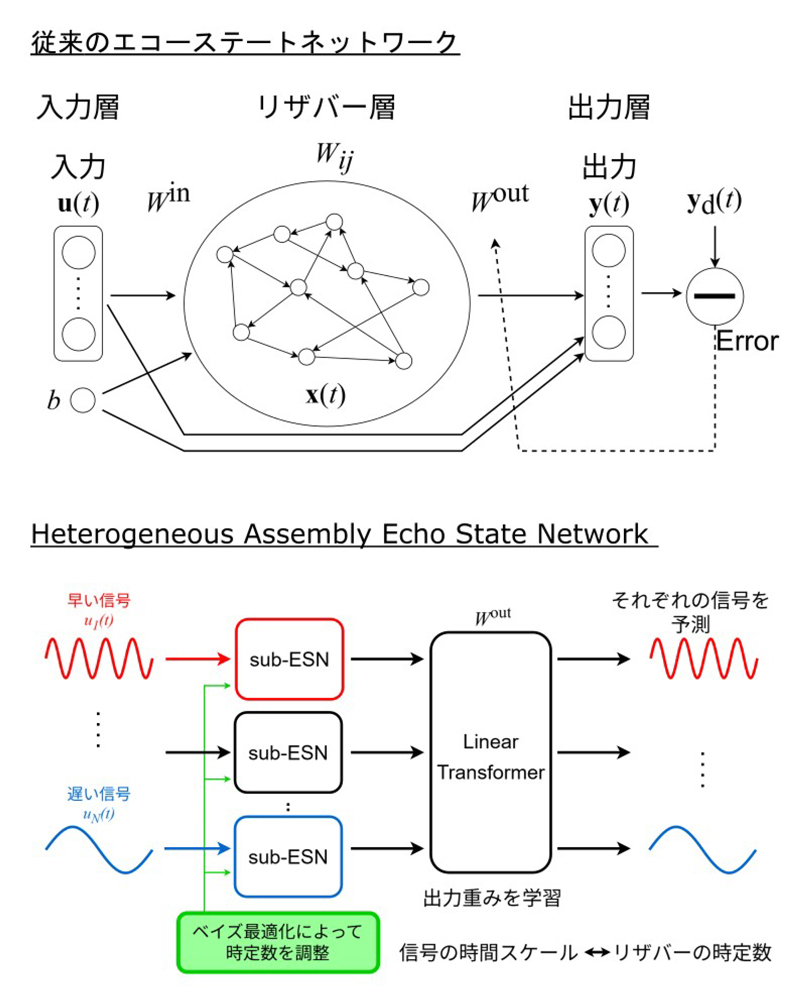
高次元マルチスケール時系列のための異種アセンブリエコー状態ネットワーク:遅延容量とマルチスケールファジィエントロピーによる動的解析 Heterogeneous Assembly Echo State Networks for High-Dimensional, Multiscale Time Series: Dynamic Analysis via Delay Capacity and Multiscale Fuzzy Entropy
Sota Yoshida; Takahiro Iinuma; Sou Nobukawa; Eiji Watanabe; Teijiro Isokawa
IEEE Access Published:03 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3639721
Abstract
Reservoir computing (RC), particularly the echo state network (ESN), is an efficient framework for time-series processing. However, its conventional form often struggles with tasks characterized by high dimensionality and multiscale temporal dynamics. We propose the heterogeneous assembly ESN (HetAESN), a novel architecture that extends the assembly ESN (AESN) by incorporating temporal heterogeneity. HetAESN partitions high-dimensional input and assigns each sub-reservoir an optimized, distinct time constant, enabling it to adapt to the specific temporal properties of its input components. We validated HetAESN using time-series prediction tasks on three chaotic systems: the two-coupled van der Pol (tc-VdP), the Hindmarsh–Rose (HR), and the two-coupled Lorenz (tc-Lorenz). HetAESN achieved superior prediction accuracy compared to conventional ESN and AESN models for the tc-VdP and HR tasks. To analyze these results, we employed delay capacity and multiscale fuzzy entropy. Our analysis revealed that the model’s effectiveness critically depends on the balance between the task’s dimensionality and the signal’s complexity within the reservoir’s effective memory range. This study clarifies the crucial relationship between architectural design—specifically dimension splitting and multiscale adaptation—and the computational capability of RC models, paving the way for developing more robust, generalized architectures for processing high-dimensional, multiscale time series.



