2025-12-18 日本原子力研究開発機構,横浜国立大学,大阪大学
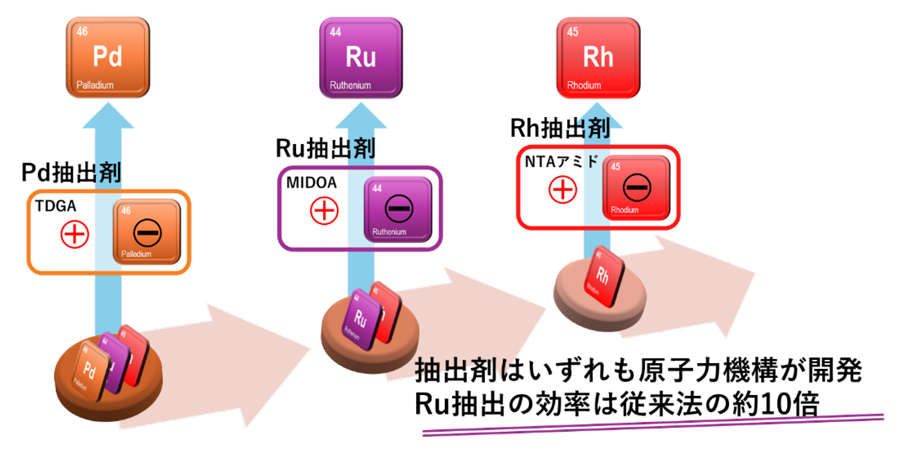
図1 開発したPd・Ru・Rhの「イオン対抽出」による分離法
<関連情報>
- https://www.jaea.go.jp/02/press2025/p25121801/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167732225021919
イオン対およびS-およびアミノ-N-ドナー試薬による溶媒和を用いた還流抽出および逆抽出によるRu、Rh、およびPdの相互分離 Mutual separation of Ru, Rh, and Pd via reflux-assisted extraction and reverse-extraction using ion-pair and solvation with S- and amino-N-donor reagents
Yuji Sasaki, Masashi Kaneko, Masahiko Matsumiya, Yuta Kumagai
Journal of Molecular Liquids Available online: 29 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2025.129013
Highlights
- We found ion-pair extraction between anions of PGM-Cl complex and protonated
- Extractant, which has a secondary or a tertiary nitrogen atom.
- We found the increase of D(PGM) by long-time refluxing, which suggests forming more chlorinated PGM ions. We confirmed it to use UV spectrum.
- We found D(Ru) = 100, very high distribution ratio of Ru, using 0.5 M NTAamide extractant from 1 M HCl.
- We found the order of PGM extractability to be NTAamide > MIDOA or IDOA > IDCA, which follows the trend of tetra > tri > bi-dentate ligand.
- We compared the extractability of N-donor with S-donor ligands and found that N-donor extractants have higher D(PGM) than S-donor’s.
- We found suitable conditions on PGM stripping.
- We showed the flow-sheet of mutual separation of Ru, Rh and Pd, by solvent extraction and reverse-extraction methods.
- We revised this paper following the reviewer’s comments.
Abstract
This study determined extraction and back-extraction conditions for the mutual separation of three light PGMs—Ru, Rh, and Pd. Results revealed that reagents containing soft N and S donor atoms efficiently extract and strip Pd through solvation. In comparison, Ru and Rh undergo ion-pair extraction, requiring both anionic metal species and cationic extractants to achieve high distribution ratios (D). These essential chlorinated PGM anions and protonated extractants having amino N atoms are present in HCl media. D(Ru) and D(Rh) values of approximately 100 and 10, respectively, were obtained using nitrilo-triacet-amide (NTAamide), which exhibits tetradentate coordination. Refluxing in 3–6 M HCl at 250 °C, a condition that promotes the formation of highly chlorinated PGM anionic species, increased D(Ru) and D(Rh). Additionally, Ru and Rh exhibited low reactivity with S-donor extractants, allowing Pd to be selectively extracted from a mixture of the three PGMs in HCl media using thio-reagents. Ru was extracted with separating Rh by methyl-imino-di-octyl-acetamide, a tridentate ligand, and was subsequently stripped using ethylenediamine and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Finally, Rh, the least reactive of the three metals, was extracted using NTAamide after refluxing in 6 M HCl for 60 min and was stripped using ethylenediamine. Based on these findings, a flow diagram for the mutual separation of the aforementioned three PGMs was developed. Thus, novel amino-amide extractants with multidentate coordination play a crucial role in PGM recovery and isolation, while stripping can be efficiently performed using commercially available reagents.



