2025-12-09 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/earth/202512/t20251210_1135817.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41558-025-02486-9
地球温暖化により、中低緯度地域では日々の気温変化が激しくなる Global warming intensifies extreme day-to-day temperature changes in mid–low latitudes
Qi Liu,Congbin Fu,Zhongfeng Xu & Aijun Ding
Nature Climate Change Published:21 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-025-02486-9
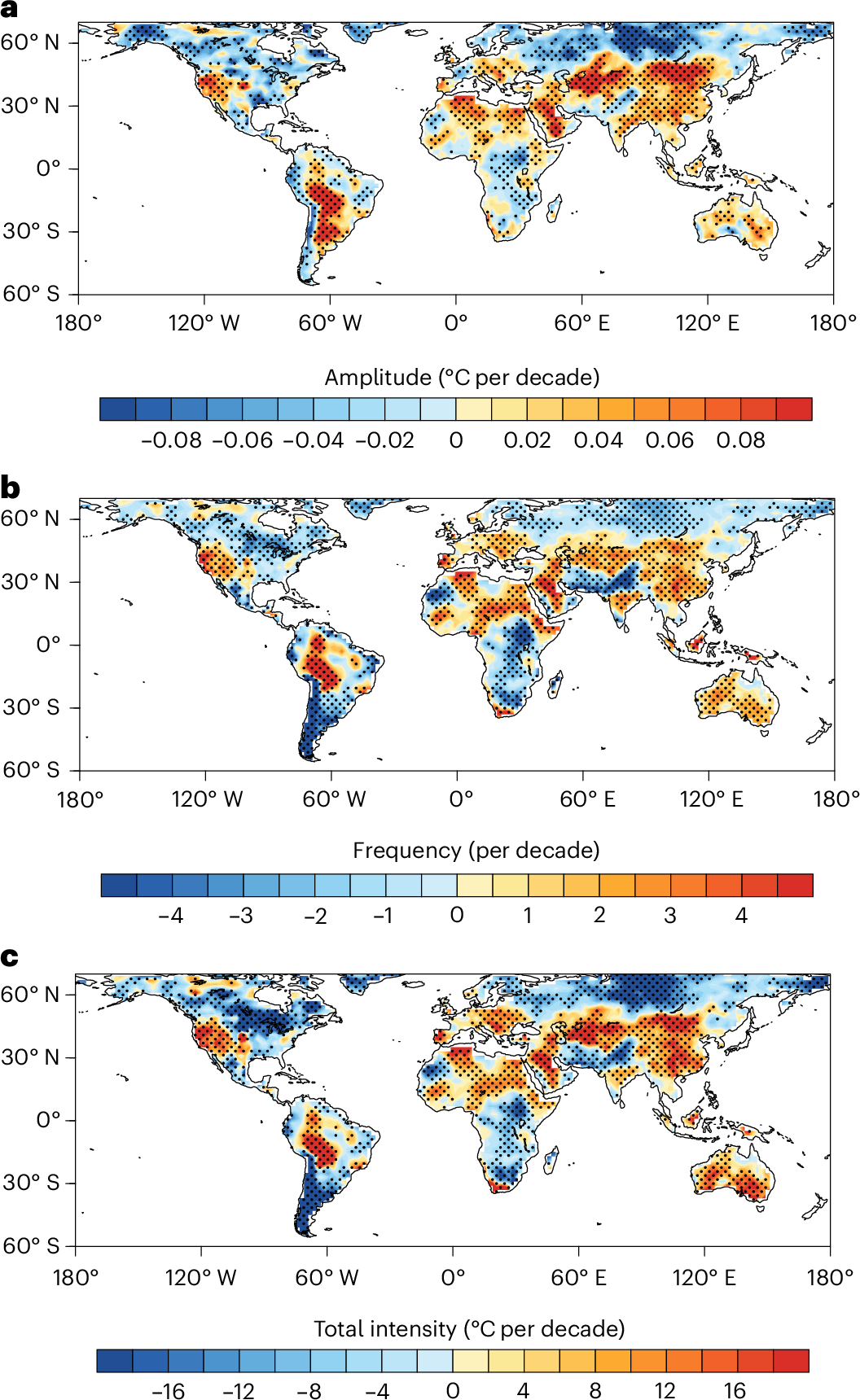
Abstract
Global warming is increasing the number and intensity of many extreme weather and climate events. Here we argue that extreme day-to-day temperature changes, exceeding the 90th percentile threshold of historical records, are an independent, but largely ignored, aspect of extreme weather events. Such extreme temperature changes have a stronger impact on human health in many locations than do diurnal temperature variations. Global observations show that such events have become more frequent since the 1960s in low and mid-latitudes but decreased at high latitudes, primarily due to GHG forcing. Climate models project a further amplification of extreme day-to-day temperature changes under warming, with frequency, amplitude and total intensity rising by ~17%, ~3% and ~20%, respectively, by 2100 in regions covering 80% of global population. Increased extreme day-to-day temperature changes are associated with drier soil and increased variability in pressure and soil moisture, posing substantial risks to societal and ecosystem resilience and adaptation.