2025-09-19 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/earth/202509/t20250922_1055118.shtml
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-025-07823-4
北大西洋海面水温ダイポールがチベット高原北部における夏季降水量の年々変動を調節する North Atlantic SST dipole modulates the interannual variability of summer precipitation over northern Tibetan Plateau
Shijie Tang,Tianjun Zhou,Jie Jiang & Wanheng Ye
Climate Dynamics Published:12 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-025-07823-4
Abstract
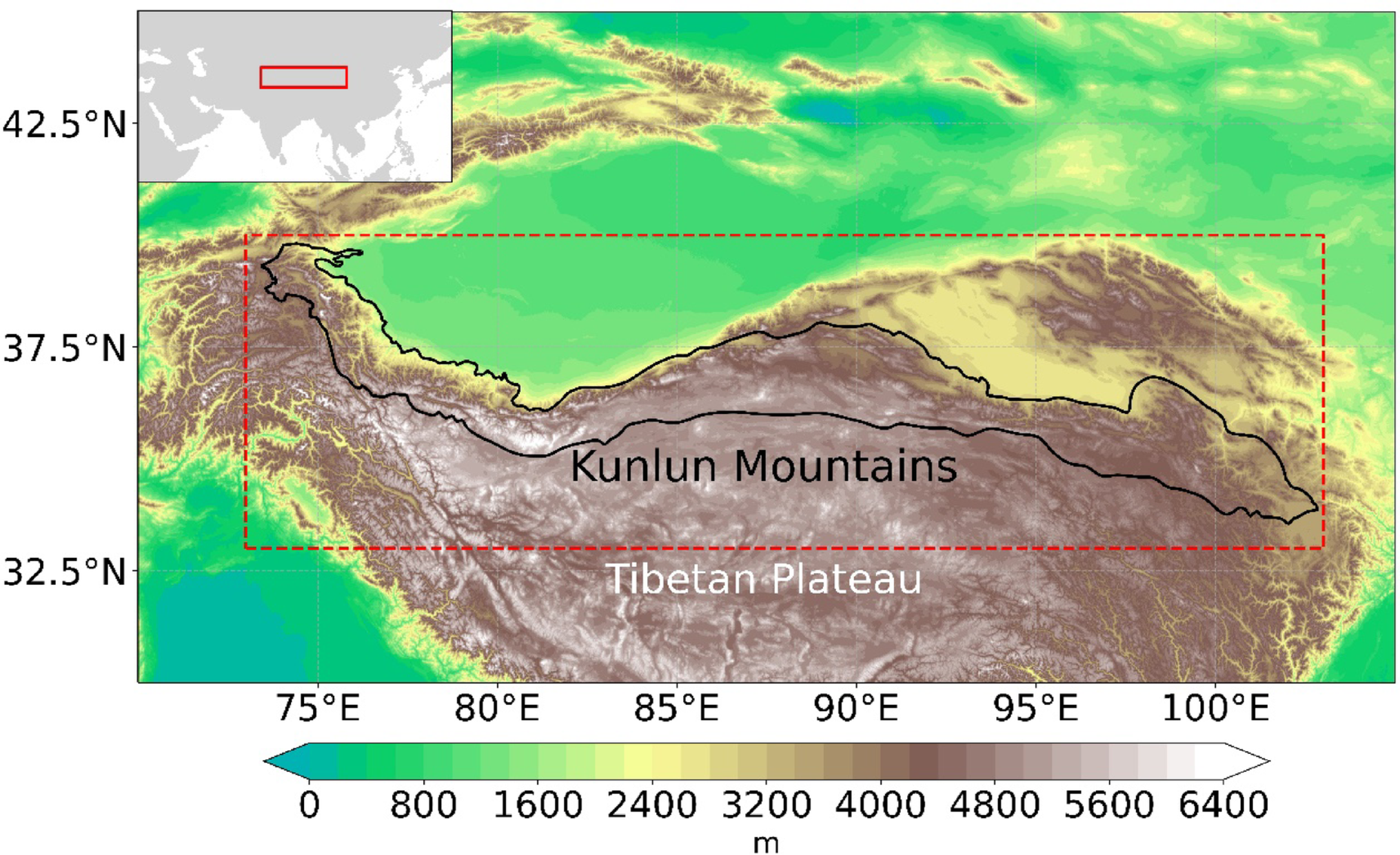
Along the northern Tibetan Plateau, the Kunlun Mountains are a principal hydrological regulator for the Tarim Basin, with precipitation variability shaping water availability and downstream geological hazards. However, the factors and the underlying physical mechanisms driving the interannual variability of precipitation remain poorly understood. Here, we investigate the interannual variability of summer precipitation in the Kunlun Mountains and its surrounding (KMS) region by combining observation and reanalysis datasets. The results show that summer precipitation in the KMS region exhibits significant interannual variability, accounting for 77% of total summer precipitation variability. It features a dominant 3-year cycle, with variability decreasing from southeast to northwest and a maximum magnitude of 52.8 mm/a. The interannual variability of summer precipitation in the KMS region is driven by an anomalous North Atlantic sea surface temperature dipole, which generates a downstream-propagating Rossby wave and induces an anomalous cyclonic circulation in the west of the KMS region. This circulation anomaly further induces anomalous meridional winds over the KMS region, enhancing horizontal water vapor convergence and dynamically modulating regional precipitation. Our findings provide new insights into the mechanisms driving precipitation variability in the KMS region, contributing to broader efforts in climate adaptation and sustainable development in arid and semi-arid regions.



