2025-09-01 東北大学
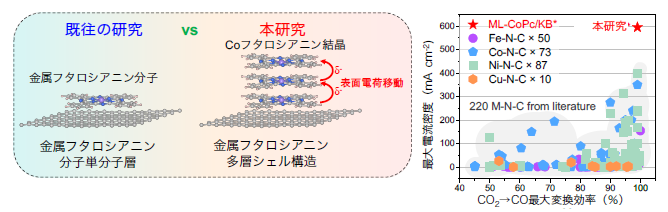
図1.コバルトフタロシアニン(CoPc)多層シェル構造を有する触媒と既往の錯体分子触媒を用いたCO2→CO研究との比較。
<関連情報>
- https://www.tohoku.ac.jp/japanese/2025/09/press20250901-04-co2.html
- https://www.tohoku.ac.jp/japanese/newimg/pressimg/tohokuuniv-press20250901_04web_co2.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0926337325008355
単一分子パラダイムの打破:CO2からCOへの電気化学的還元における優れた活性単位としての多層コバルトフタロシアニン/カーボンコアシェル構造 Breaking the single-molecule paradigm: Multilayer cobalt phthalocyanine/carbon core-shell structure as the superior active unit for CO2-to-CO electroreduction
Tengyi Liu, Di Zhang, Yue Chu, Keitaro Ohashi, Yutaro Hirai, Koju Ito, Kosuke Ishibashi, Yasutaka Matsuo, Junya Yoshida, Shimpei Ono, Kazuhide Kamiya, Hao Li, Hiroshi Yabu
Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy Available online: 17 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2025.125852
Highlights
- Developed multilayer CoPc/carbon structure with superior active units for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction.
- AI-powered large-scale data mining of 220 M-N-C materials guided electrocatalyst selection.
- Achieved ultrahigh CO current density of ‐595 mA cm-2, mass activity of 6537 A g-1, and 100 h stability for CO electrosynthesis.
- Further AIP-LDM confirms that our performance metrics surpass all previously reported Pc-based catalysts.
- Surface charge transfer and structural advantages of multilayer CoPc/KB hybrid boost intrinsic activity and catalytic efficiency.
Abstract
Conventional “chemical intuition” attributes the electrocatalytic activity of phthalocyanines (Pc) to idealized single-molecule/carbon models, however, we reveal that a multilayer Pc/carbon architecture more accurately reflects the true active units. Using AI-powered large-scale data mining (AIP-LDM), we examined 220 metal-nitrogen-carbon (M-N-C) materials for CO2-to-CO electroreduction, identifying cobalt-phthalocyanine (CoPc) as a promising candidate. When integrated with Ketjen Black (KB), the resulting CoPc/KB electrode achieves a large CO current density of −595 mA cm−2 and a high mass activity of 6537 A g−1, while maintaining > 90 % CO selectivity at −100 mA cm−2 for 100 h. Comprehensive analyses reveal CoPc molecules form polycrystalline layers on KB, creating a multilayer CoPc/carbon core-shell structure that induces surface charge transfer (SCT). Theoretical calculations confirm even minimal SCT significantly enhances intrinsic activity. Further AIP-LDM findings show our hybrid surpasses all reported Pc-based catalysts, highlighting this multilayer Pc/carbon architecture’s advantages and affirming its strong industrial potential in Pc materials.



