2025-08-27 北海道大学
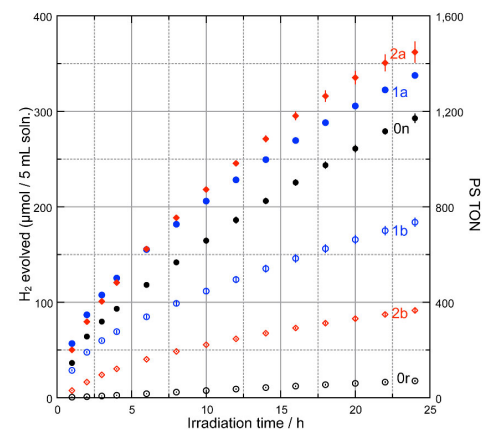
図 1. ⾊素担持条件を変えた PRCC 系(6 種類)の(横軸)光照射時間に対する(縦軸左)⽣成⽔素量及び⾊素1分⼦あたりの触媒回転数(縦軸右:PS TON)のプロット
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/2025/08/post-2033.html
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/250827_pr.pdf
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2025/su/d5su00054h
Photocatalytic dissolution of cellulose for hydrogen and nanofiber production: unveiling crucial factors via experiments and informatics セルロースの光触媒的溶解による水素とナノファイバー生産:実験とインフォマティクスに基づく重要因子の解明
Atsushi Kobayashi, Atsushi Miura and Keisuke Takahashi
RSC Sustainability Published:26 Aug 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SU00054H
Abstract
The efficient utilization of biomass resources and solar energy is necessary for next-generation sustainable carbon-neutral societies. Although cellulose is the most abundant biomass on Earth, its utilization as a carbon resource is hampered by its strongly stabilized polymer-bundled structure. In this study, a new photoredox cascade catalyst (PRCC) conversion system was developed by combining dual-dye-sensitized Pt-cocatalyst-loaded TiO2 nanoparticle photocatalysts (DDSPs) and a 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl (TEMPO) oxidation catalyst for the production of cellulose nanofibers and hydrogen from various cellulose substrates (powder, paper, sponge, and wood pellets) under blue light irradiation without the use of strong acids/bases. UV-vis absorption and emission spectroscopy revealed that the loaded amount of the Ru(II) dye on the TiO2 surface was successfully controlled in the range of 353–667 nmol/1 mg TiO2, and the immobilization order of two Ru(II) dyes significantly affected the energy- and electron-transfer behaviors between the Ru(II) dyes and TiO2 nanoparticles. Our systematic evaluation of the photocatalytic activity and machine learning analysis of 12 different DDSPs revealed that the immobilization order of the two Ru(II) dyes, full coverage of the TiO2 nanoparticle surface with suitable Ru(II) dye molecules, and Zr4+ cation loading are crucial factors for achieving a high apparent quantum yield for the hydrogen-evolving PRCC conversion of cellulose to nanofibers (max. 1.62% at 467 nm excitation for the initial 1 h of reaction in a 0.3 M cellulose aqueous dispersion). The findings contribute to the development of an environmentally benign photocatalytic approach for the conversion of cellulosic biomass as a carbon resource into valuable organic products.



