2025-08-15 カリフォルニア大学ロサンゼルス校(UCLA)

Riyaaz Shaik and Patrick Hadinata/UCLA
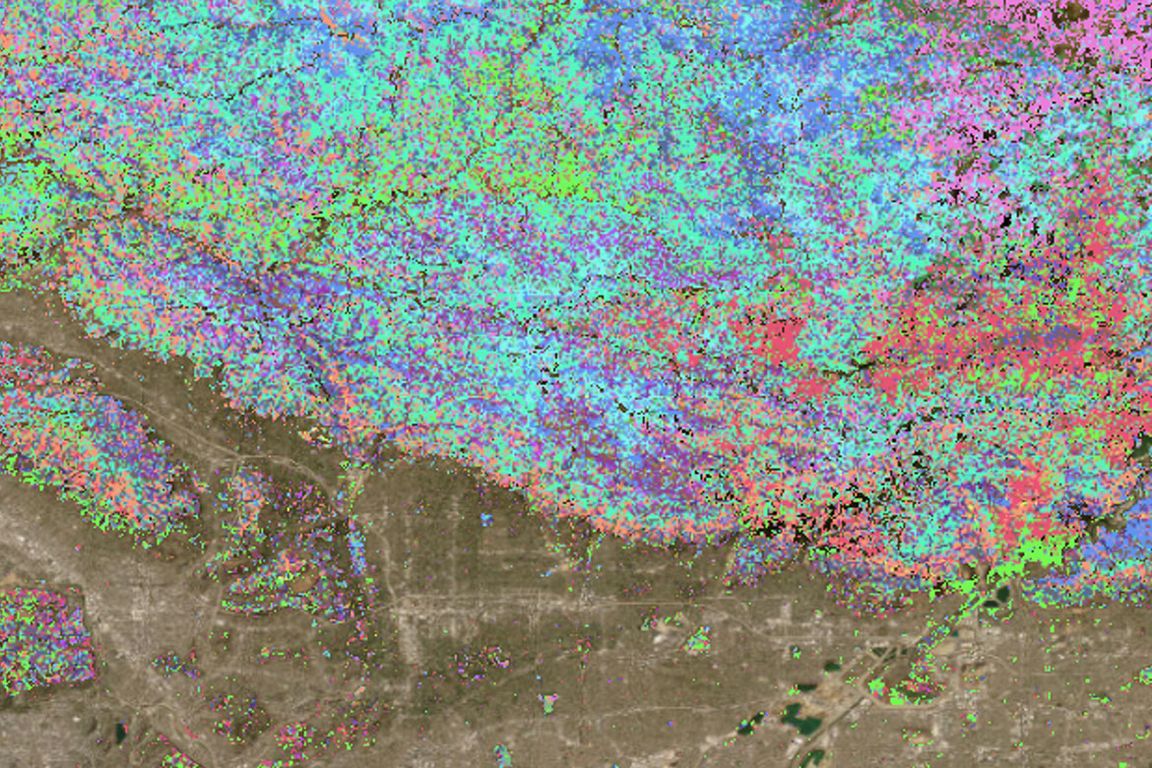
Fuels map of the 2025 Eaton Fire, as predicted by FuelVision.
<関連情報>
- https://newsroom.ucla.edu/stories/ai-powered-tool-wildfire-fuel-mapping-fuelvision-ucla
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1569843225000834
FUELVISION:山火事燃料マッピングのためのマルチモーダルデータ融合とマルチモデルアンサンブルアルゴリズム FUELVISION: A multimodal data fusion and multimodel ensemble algorithm for wildfire fuels mapping
Riyaaz Uddien Shaik, Mohamad Alipour, Eric Rowell, Bharathan Balaji, Adam Watts, Ertugrul Taciroglu
International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation Available online: 12 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2025.104436
Highlights
- Near real-time wildland fuels mapping algorithm.
- Leverage satellite remote sensing data and terrain features.
- Overcome challenge posed by imbalanced datasets.
- Leverage General Adversarial Networks for synthetic remote sensing data generation.
Abstract
Accurate assessment of fuel conditions is a prerequisite for fire ignition and behavior prediction, and risk management. The method proposed herein leverages diverse data sources – including L8 optical imagery, S1 (C-band) Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery, PL (L-band) SAR imagery, and terrain features – to capture comprehensive information about fuel types and distributions. An ensemble model was trained to predict landscape-scale fuels – such as the ’Scott and Burgan 40’ – using the as-received Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA) field survey plot data obtained from the USDA Forest Service. However, this basic approach yielded relatively poor results due to the inadequate amount of training data. Pseudo-labeled and fully synthetic datasets were developed using generative AI approaches to address the limitations of ground truth data availability. These synthetic datasets were used for augmenting the FIA data from California to enhance the robustness and coverage of model training. The use of an ensemble of methods – including deep learning neural networks, decision trees, and gradient boosting – offered a fuel mapping accuracy of nearly 80%. Through extensive experimentation and evaluation, the effectiveness of the proposed approach was validated for regions of the 2021 Dixie and Caldor fires. Comparative analyses against high-resolution data from the National Agriculture Imagery Program (NAIP) and timber harvest maps affirmed the robustness and reliability of the proposed approach, which is capable of near-real-time fuel mapping.