2025-08-12 マックス・プランク研究所

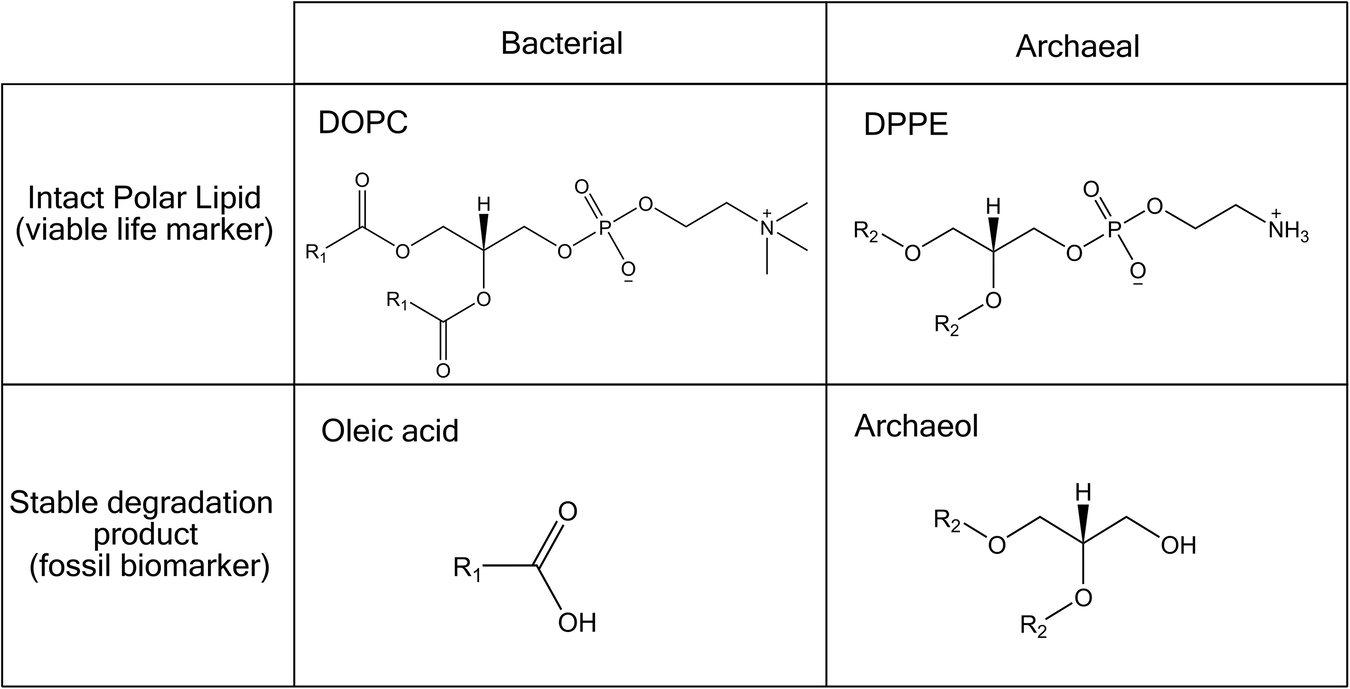
Looking inside the plasma jet cone of the blazar PKS 1424+240 with a radio telescope of the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA). © NSF/AUI/NRAO/B. Saxton/Y.Y. Kovalev et al.
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/25171297/eye-of-sauron-in-deep-space
- https://www.aanda.org/articles/aa/full_html/2025/08/aa55400-25/aa55400-25.html
ニュートリノ関連の高エネルギーブラザールPKS 1424+240のジェットコーンの解析 Looking into the jet cone of the neutrino-associated very high-energy blazar PKS 1424+240
Y. Y. Kovalev, A. B. Pushkarev, J. L. Gómez, D. C. Homan, M. L. Lister, J. D. Livingston, I. N. Pashchenko, A. V. Plavin, T. Savolainen and S. V. Troitsky
Astronomy & Astrophysics Published:12 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202555400
Abstract
Context. The acceleration process of massive particles as well as the production of very high-energy (VHE) photons and neutrinos remains a fundamental challenge in astrophysics.
Aims. We investigate the parsec-scale jet structure and magnetic field of the blazar PKS 1424+240, which was selected on the basis of strong VHE gamma-ray emission and is identified with one of the highest peaks in the IceCube 9-year neutrino sky.
Methods. We analyzed 15 GHz VLBA observations of this BL Lac object by stacking 42 polarization-sensitive images collected in 2009–2025 to enhance the signal and reveal the persistent parsec-scale structure.
Results. Our observations uncover a rare scenario. The object is viewed inside the jet cone, very close to the axis of its relativistic jet, with a viewing angle of < 0.6°. This effectively maximizes Doppler boosting to values ∼30 and enhances the electromagnetic and neutrino emission in the direction of the observer. Based on polarimetric observations, we unambiguously detect a net toroidal component in the magnetic field of the jet. This indicates a current-carrying jet that flows almost directly toward our line of sight.
Conclusions. Blazars with very small jet viewing angles offer a solution to the Doppler factor crisis, i.e., to the longstanding mismatch between Doppler factors inferred from the low apparent jet speed in very long-baseline interferometry and those derived from VHE observations. We show that relativistic beaming plays the critical role in the gamma-ray and neutrino emission of blazars. This has direct implications for models of their multimessenger emission.