2025-07-29 森林総合研究所
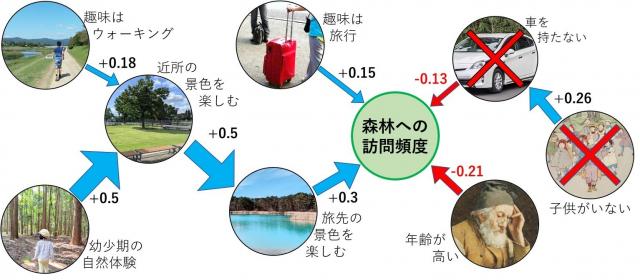
図1 森林への訪問に結びつく要因と、その因果関係
<関連情報>
- https://www.ffpri.go.jp/press/2025/20250729/index.html
- https://www.ffpri.go.jp/press/2025/20250729/documents/20250729press.pdf
- https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4907/16/5/714
森林への関心と訪問を左右する主要因の解明:持続可能な森林利用に向けた効果的な戦略の構築を目指して Unveiling Key Factors Shaping Forest Interest and Visits: Toward Effective Strategies for Sustainable Forest Use
Kimisato Oda,Kazushige Yamaki,Asako Miyamoto,Keita Otsuka,Shoma Jingu,Yuichiro Hirano,Mariko Inoue,Toshiya Matsuura,Kazuhiko Saito andNorimasa Takayama
Forests Published: 23 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050714
Abstract
This study investigates the factors influencing urban residents’ interest in and visits to forests and explores strategies to promote forest space utilization. A survey was conducted among 5000 residents of Tokyo’s 23 wards, one of the world’s most densely populated urban areas, using an online questionnaire. The collected data were analyzed using least absolute shrinkage, selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression, and piecewise structural equation modeling (pSEM). The analysis revealed that nature experiences in current travel destinations, particularly scenic walks, had a significant positive effect on both forest interest (standardized path coefficient = 0.19) and forest visits (0.30). These experiences were also significantly influenced by childhood nature experiences and frequent local walks. Conversely, factors negatively affecting forest visits included the lack of private vehicle ownership (−0.13) and increasing age (−0.21). While previous studies suggest that older individuals tend to visit natural areas more frequently, our findings indicate the opposite trend. One possible explanation is the low car ownership rate among Tokyo residents, which may limit accessibility to forests. These findings provide valuable insights for policy design, particularly regarding strategies to enhance forest accessibility and engagement among urban populations.