2025-07-25 東京科学大学
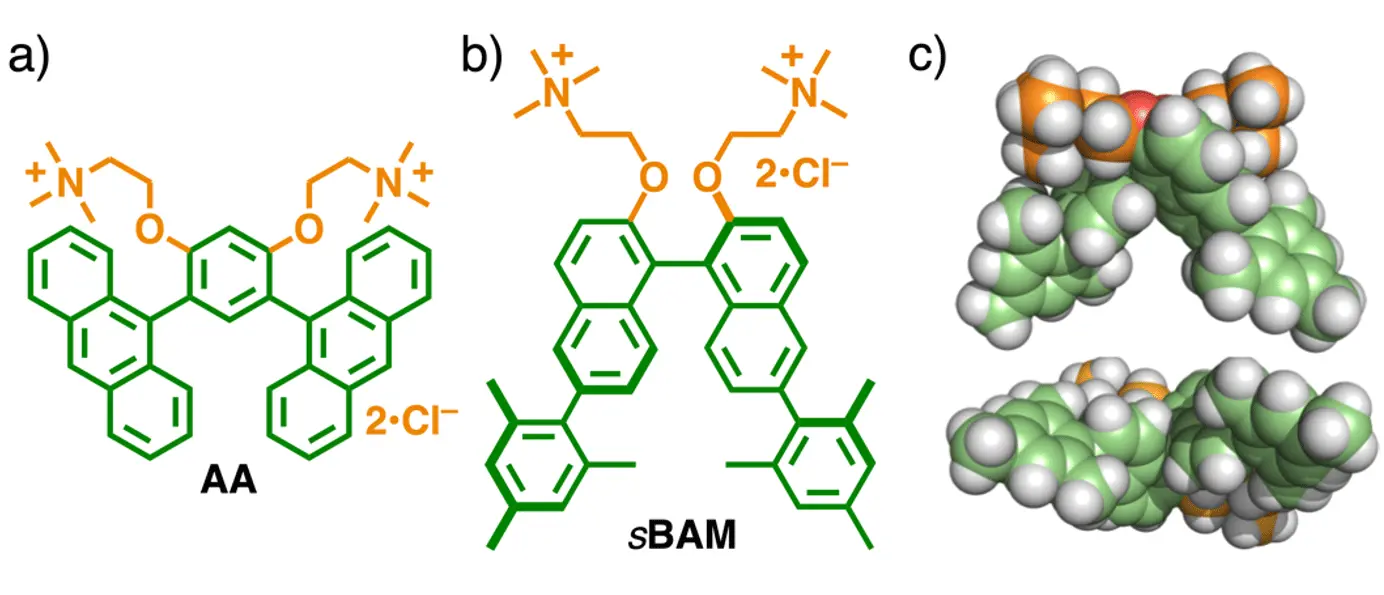
図1.a)既報の非キラルな湾曲型両親媒性分子AA、 b)本研究のキラルな湾曲型両親媒性分子sBAMと c)その計算構造。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/veh6km416qnb
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=1969&prevId=&key=43a7ffee367e442c2e33a5c792045daf.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c06179
水中の大型金属色素のキラル光学ホストツールとしてのキラル芳香族ミセル Chiral Aromatic Micelles as Chiroptical Host Tools for Large Metallodyes in Water
Yoshihisa Hashimoto,Yuya Tanaka,Si-Yu Liu,Hiroshi Shinokubo,and Michito Yoshizawa
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: June 15, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c06179
Abstract
In contrast to abundant aliphatic chiral cavities in nature, synthetic chiral cavities formed by self-assembly of aromatic subunits are quite rare, particularly providing an ability in induced chirality. Here, we report new chiral aromatic micelles capable of inducing the optical chirality of large metallodyes upon encapsulation. The aromatic micelle, with a core diameter of ∼3 nm, forms from axially chiral amphiphiles featuring a bent mesityl-substituted BINOL framework. Unlike alkyl and aromatic micelles reported previously, the obtained micelle emits strong fluorescence (ΦF > 40%) through the aggregation-induced emission effect in water. The adaptable chiral cavity of the micelle efficiently encapsulates several kinds of achiral metallodyes, such as metalated porphyrins and norcorroles, to afford aqueous host–guest composites, displaying efficient dye-based induced chirality through multiple CH-π interactions. Remarkably, the chirality induction of metallophthalocyanine, bearing a completely planar framework, and its stacked dimer can also be demonstrated (up to |gabs| = 2.4 × 10–3) in the cavity under ambient aqueous conditions. To the best of our knowledge, the present aromatic micelles are the first host tools to induce the chiral properties of common to rare metallodyes, without additional covalent functionalizations. The chiroptical properties of the obtained host–guest composites are further tunable (i.e., 0.1- to 1.6-fold intensity) upon thermal stimuli in an irreversible fashion without disassembly.