2025-05-20 ワシントン州立大学(WSU)
<関連情報>
- https://news.wsu.edu/press-release/2025/05/20/wild-spinach-offers-path-to-breed-disease-resistance-into-cultivated-varieties/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-98932-x
Spinacia turkestanicaにおける萎凋病抵抗性のゲノムワイド関連研究 Genome wide association study of Fusarium wilt resistance in Spinacia turkestanica
Sanjaya Gyawali,Gehendra Bhattarai,James C. Correll,Ainong Shi & Lindsey J. du Toit
Scientific Reports Published:03 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-98932-x
Abstract
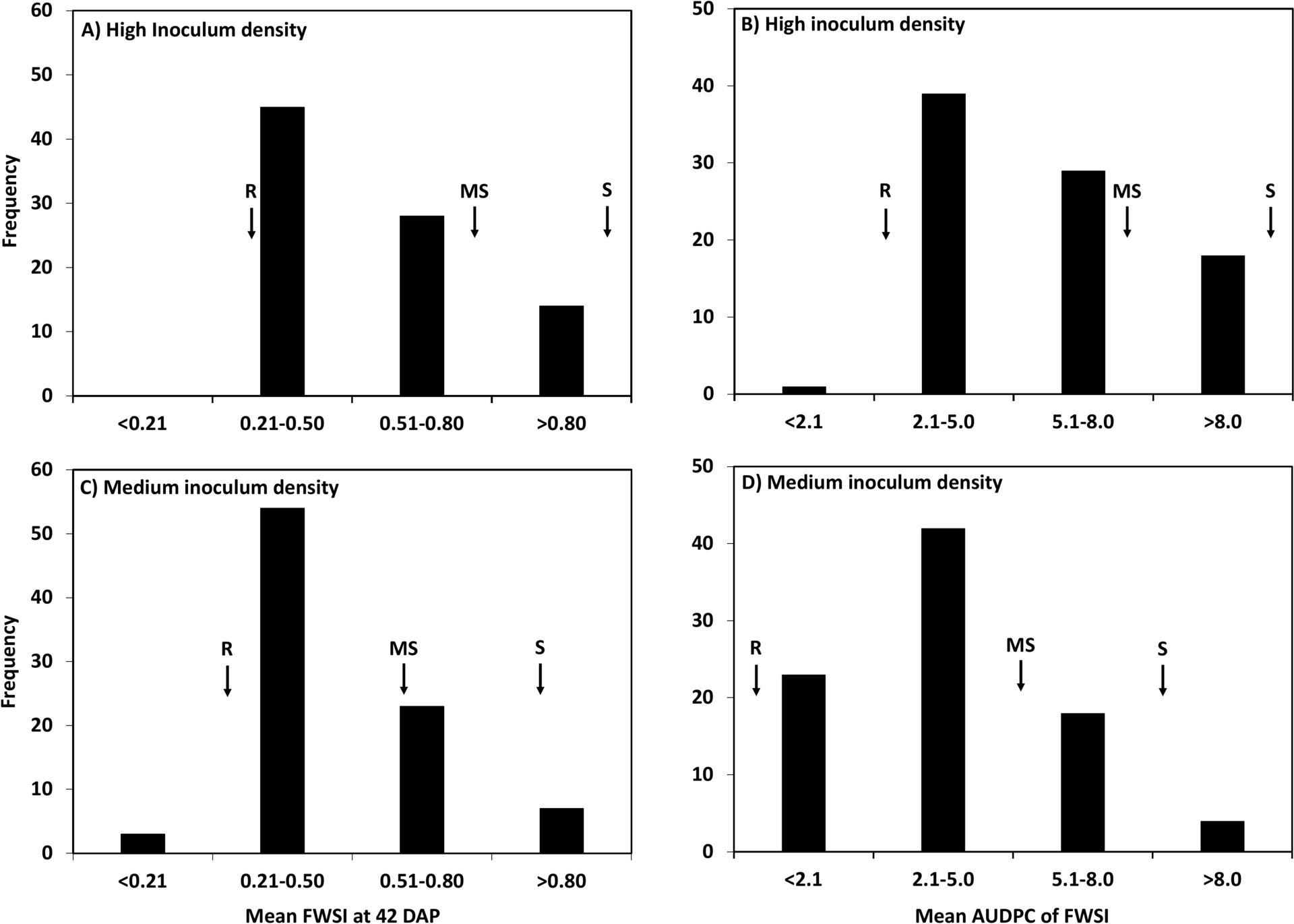
Fusarium wilt of spinach, caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. spinaciae (Fos), leads to substantial losses in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) seed production in the only region of the USA suitable for growing spinach seed crops, the maritime Pacific Northwest. Accessions of wild spinach, S. turkestanica, serve as a major source of resistance to multiple spinach diseases. In this study, 84 Spinacia genotypes (all 68 S. turkestanica accessions available publicly and 16 S. oleracea) were evaluated for reactions to Fos at medium and high densities of inoculum comprising a mix of isolates of races 1 and 2, using a factorial experimental design of genotypes (n = 84) and Fos inoculum density (0, 12,500, and 37,500 CFU/ml potting medium) with two replicates. The area under the disease progress curve (AUDPC) calculated for wilt severity 28, 35, and 42 days after planting (DAP) ranged from 0.0 to 11.0 and 1.5 to 13.3 at medium and high inoculum densities, respectively. Of the 68 S. turkestanica accessions, 17 and 8 showed high levels of resistance at medium and high inoculum densities, respectively. Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers (n = 7,065) identified with genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) were used for genome wide association studies (GWAS) using multiple models tested with GAPIT and TASSEL software. Twelve SNPs were associated significantly with Fusarium wilt resistance in 10 QTL regions located on chromosomes 1, 3, 4, and 6. SNP S6_38110665 on chromosome 6 was validated across multiple GWAS models and demonstrated a major effect (-2.48 to -2.79) at reducing Fusarium wilt severity. SNP S6_38110665 can be used to introduce Fusarium wilt resistance QTL into cultivated spinach (S. oleracea) using marker-assisted selection, thereby enhancing breeding programs for improved disease resistance.