2025-04-30 東北大学,量子科学技術研究開発機構,兵庫県立大学,産業技術総合研究所,物質・材料研究機構
物質・材料研究機構(NIMS)などの研究チームは、3GeV高輝度放射光施設「NanoTerasu」の共用ビームラインで開発された世界最高性能の共鳴非弾性X線散乱(RIXS)を用いて、−163℃で超伝導を示す銅酸化物高温超伝導体中の電子のプラズマ振動の性質を解明しました。この成果は、超伝導発現機構の理解や転移温度の向上に寄与することが期待されます。
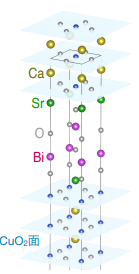
図 1. 本研究で測定した三層系銅酸化物 Bi2Sr2Ca2Cu3O10 の結晶構造。超伝導が発現する二次元的な CuO2面が三枚ずつ積み重なる構造を持つ。
<関連情報>
- https://www.nims.go.jp/press/2025/04/202504300.html
- https://www.tohoku.ac.jp/japanese/newimg/pressimg/tohokuuniv-press20250430_03_plasmon.pdf
- https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.111.165141
三層銅酸化物Bi2Sr2Ca2Cu3O10+δにおける位相のずれたプラズモン励起 Out-of-phase plasmon excitations in the trilayer cuprate Bi2Sr2Ca2Cu3O10+δ
S. Nakata, M. Bejas, J. Okamoto, K. Yamamoto, D. Shiga, R. Takahashi, H. Y. Huang, H. Kumigashira, H. Wadati et al.
Physical Review B Published: 21 April, 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.111.165141
Abstract
Within a homologous series of cuprate superconductors, variations in the stacking of CuO2 layers influence the collective charge dynamics through the long-range Coulomb interactions. We use O -edge resonant inelastic x-ray scattering to reveal plasmon excitations in the optimally doped trilayer Bi2Sr2Ca2Cu3O10+δ. The observed plasmon exhibits nearly qz-independent dispersion and a large excitation gap of approximately 300 meV. This mode is primarily ascribed to the ω− mode, where the charge density on the outer CuO2 sheets oscillates out of phase while the density in the inner sheet remains unaltered at qx=0. The intensity of the acoustic ω3 mode is relatively weak and becomes vanishingly small near (qx,qy)=(0,0). This result highlights a qualitative change in the eigenmode of the dominant low-energy plasmon with the number of CuO2 layers.



