2025-04-25 英国研究イノベーション機構(UKRI)
<関連情報>
- https://www.ukri.org/news/pea-breakthrough-could-transform-global-farming-and-sustainability/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-08891-6
メンデルのエンドウ豆遺伝子のゲノムと遺伝学的洞察 Genomic and genetic insights into Mendel’s pea genes
Cong Feng,Baizhi Chen,Julie Hofer,Yan Shi,Mei Jiang,Bo Song,Hong Cheng,Lu Lu,Luyao Wang,Alex Howard,Abdel Bendahmane,Anissa Fouchal,Carol Moreau,Chie Sawada,Christine LeSignor,Cuijun Zhang,Eleni Vikeli,Georgios Tsanakas,Hang Zhao,Jitender Cheema,J. Elaine Barclay,Junliang Hou,Liz Sayers,Luzie Wingen,… Shifeng Cheng
Nature Published:23 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-08891-6
Abstract
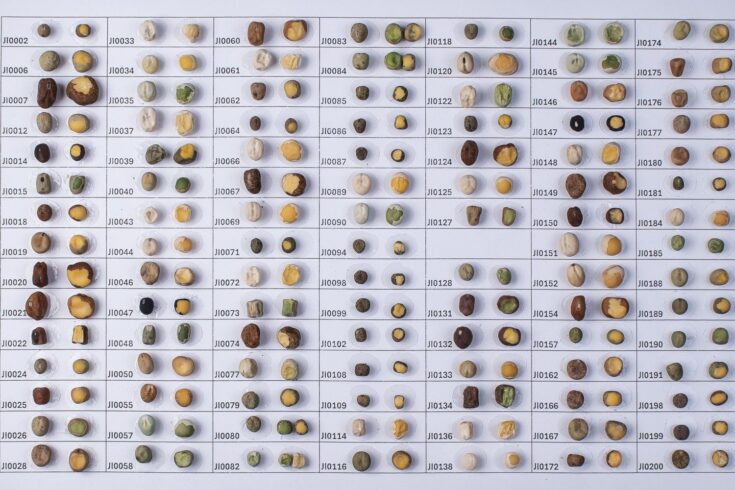
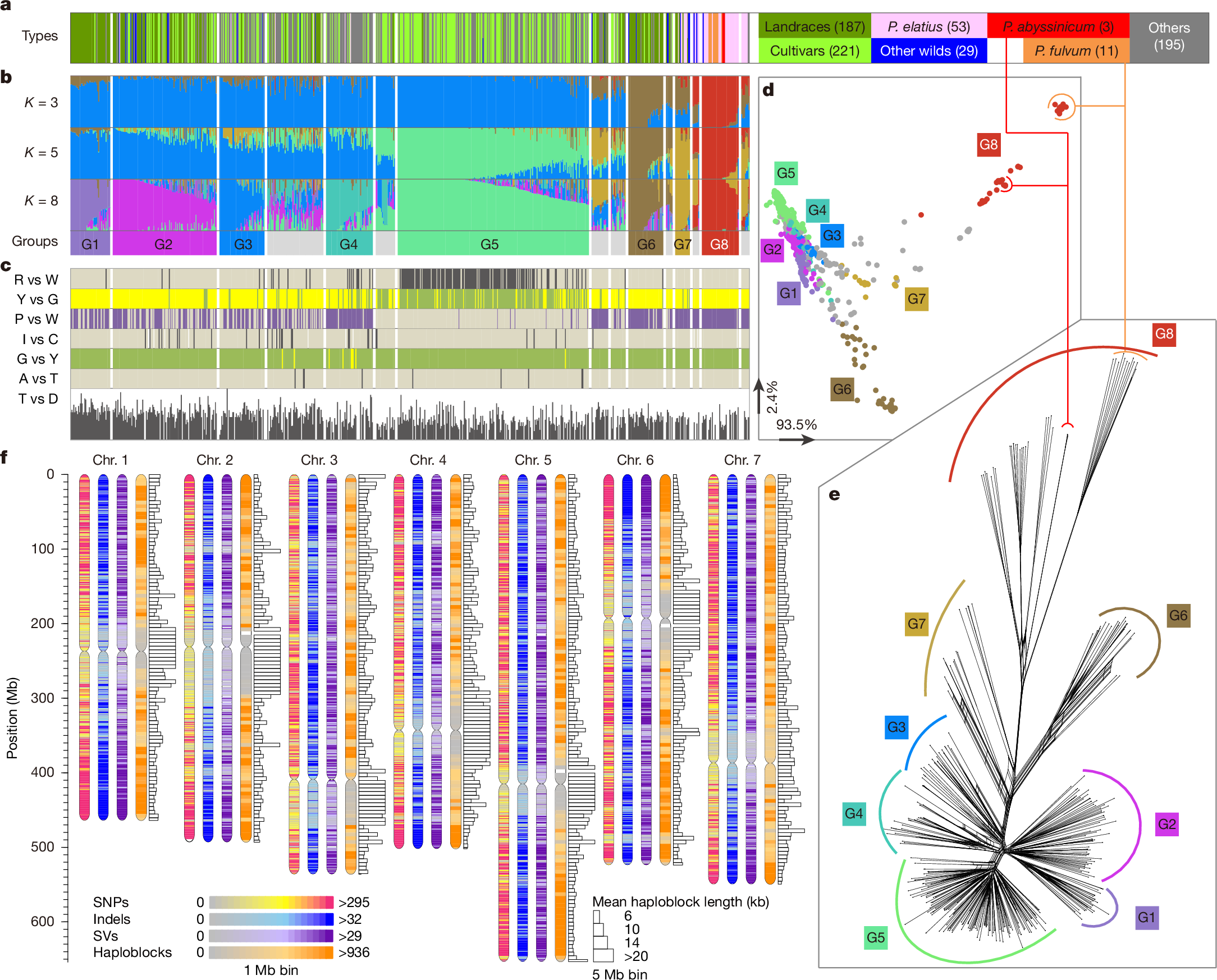
Mendel1 studied in detail seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea (Pisum sativum), establishing the foundational principles of genetic inheritance. Here we investigate the genetic architecture that underlies these traits and uncover previously undescribed alleles for the four characterized Mendelian genes2,3,4,5,6,7, including a rare revertant of Mendel’s white-flowered a allele. Primarily, we focus on the three remaining uncharacterized traits and find that (1) an approximately 100-kb genomic deletion upstream of the Chlorophyll synthase (ChlG) gene disrupts chlorophyll biosynthesis through the generation of intergenic transcriptional fusion products, conferring the yellow pod phenotype of gp mutants; (2) a MYB gene with an upstream Ogre element insertion and a CLE peptide-encoding gene with an in-frame premature stop codon explain the v and p alleles, which disrupt secondary cell wall thickening and lignification, resulting in the parchmentless, edible-pod phenotype; and (3) a 5-bp exonic deletion in a CIK-like co-receptor kinase gene, in combination with a genetic modifier locus, is associated with the fasciated stem (fa) phenotype. Furthermore, we characterize genes and alleles associated with diverse agronomic traits, such as axil ring anthocyanin pigmentation, seed size and the ‘semi-leafless’ form. This study establishes a foundation for fundamental research, education in biology and genetics, and pea breeding practices.