2025-03-05 中国科学院 (CAS)
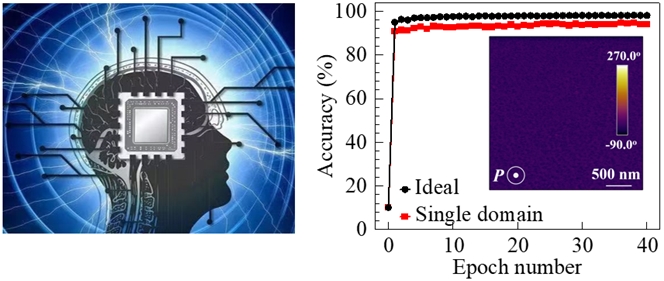
The conception of neuromorphic computing (left from Baidu) and pattern recognition accuracy of a single domain ferroelectric synapse (Image by IMR)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/tech/202503/t20250306_903226.shtml
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.202423225
高性能神経シナプスのための界面元素蓄積誘起単一強誘電体ドメイン Interface Element Accumulation-Induced Single Ferroelectric Domain for High-Performance Neuromorphic Synapse
Xiaoqi Li, Jiaqi Liu, Fan Xu, Sajjad Ali, Han Wu, Biaohong Huang, Haoyue Deng, Yizhuo Li, Yuxuan Jiang, Zhen Fan, Yunlong Tang, Yujia Wang, Mohamed Bououdina, Teng Yang, Weijin Hu, Zhidong Zhang
Advanced Functional Materials Published: 19 February 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202423225
Abstract
Ferroelectric (FE) synapses are promising for neuromorphic computing toward enhanced artificial intelligence systems. Nonetheless, there is a significant gap in understanding how to effectively tailor self-polarization and its implications on synaptic device performance. Here, an approach using interfacial element accumulation is reported to tailor the self-polarization states of BaTiO3 (BTO)/La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 (LSMO) FE heterostructure into a single domain state. This single domain configuration results are demonstrated in a gradient distribution of oxygen vacancies across the film thickness, yielding an extraordinary on/off ratio of 107 in Pt/BTO/LSMO FE diodes. This giant resistive switching enables the long-term potentiation and long-term depression synaptic functions of excellent linearity and symmetry (with a nonsymmetry factor as low as 0.1), leading to a supervised learning ability of the associated artificial neural network with a high pattern recognition accuracy of 95%. This work provides a simple design principle for FE single domain, which is substantial in enhancing the performance of FE synapses for neuromorphic computing.



