2025-02-19 ジョージア工科大学
ジョージア工科大学の研究者たちは、飲料水中の有害な「永久化学物質(PFAS)」を効果的に除去するための新しい膜の設計に取り組んでいます。PFASは化粧品、ノンスティック調理器具、食品包装などに含まれ、環境中に長期間残留し、人体内では免疫系の抑制や癌リスクの増加と関連しています。従来の水処理方法ではPFASの除去が難しいため、研究チームは機械学習モデルを活用して、PFASを効率的に分離する膜材料を特定しました。この研究は、米国農務省、国立科学財団、環境保護庁からの1,000万ドル以上の助成を受け、ウィスコンシン大学マディソン校やアリゾナ州立大学と協力して行われました。成果は『Nature Communications』誌に掲載されています。
<関連情報>
- https://research.gatech.edu/georgia-tech-research-targets-forever-chemicals-drinking-water
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-55320-9
機械学習と分子シミュレーションを用いたポリアミド膜によるPFAS除去の支配因子の解明 Elucidating governing factors of PFAS removal by polyamide membranes using machine learning and molecular simulations
Nohyeong Jeong,Shinyun Park,Subhamoy Mahajan,Ji Zhou,Jens Blotevogel,Ying Li,Tiezheng Tong & Yongsheng Chen
Nature Communications Published:30 December 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-55320-9
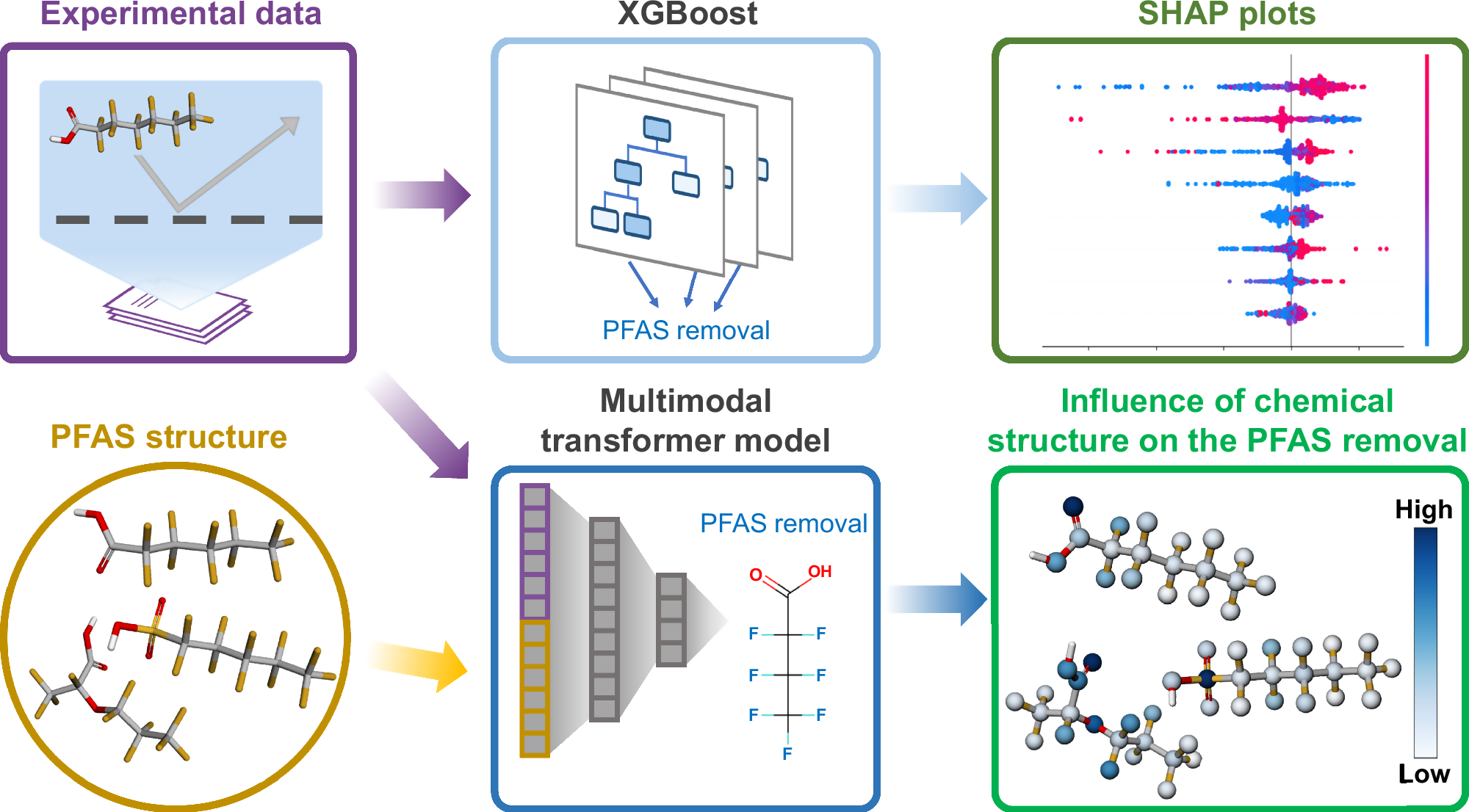
Abstract
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) have recently garnered considerable concerns regarding their impacts on human and ecological health. Despite the important roles of polyamide membranes in remediating PFASs-contaminated water, the governing factors influencing PFAS transport across these membranes remain elusive. In this study, we investigate PFAS rejection by polyamide membranes using two machine learning (ML) models, namely XGBoost and multimodal transformer models. Utilizing the Shapley additive explanation method for XGBoost model interpretation unveils the impacts of both PFAS characteristics and membrane properties on model predictions. The examination of the impacts of chemical structure involves interpreting the multimodal transformer model incorporated with simplified molecular input line entry system strings through heat maps, providing a visual representation of the attention score assigned to each atom of PFAS molecules. Both ML interpretation methods highlight the dominance of electrostatic interaction in governing PFAS transport across polyamide membranes. The roles of functional groups in altering PFAS transport across membranes are further revealed by molecular simulations. The combination of ML with computer simulations not only advances our knowledge of PFAS removal by polyamide membranes, but also provides an innovative approach to facilitate data-driven feature selection for the development of high-performance membranes with improved PFAS removal efficiency.